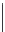Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
Oilseed
rape
Cotton
Maize
Potato
Rice
Soybean
Sugarbeet
IR
4
15
0
0
0
1
0
HT
6
11
10
0
1
18
2
HR
IR
11
35
0
1
0
2
0
Others
0
2
0
3
0
1
0
Fig. 3.1.
Number of GM plant applications submitted to the EFSA for risk assessment. The number of
GM plant applications is divided by crop species in combination with their intended traits. The traits are
denoted by pattern code: dotted = insect resistance (IR); white = herbicide tolerance (HT); dashed =
herbicide tolerance and insect resistance (HR+IR); black = traits other than IR or HT (others).
recombinant-DNA plants' (CAC, 2008), as
well as a large number of specii c commodity
standards. Codex standards, guidelines and
more information can be found at
http://
To support the CAC, ad hoc inter-
governmental task forces on food derived
from modern biotechnologies, joint FAO/
WHO expert consultations, have published
the 'Safety aspects of genetically modii ed
foods of plant origin' (WHO, 2000) and the
'Evaluation of allergenicity of genetically
modii ed foods' (WHO, 2001). Nevertheless,
neither Codex nor WHO/FAO documents
specii cally address the use of GM plants for
the production of animal feed.
h e Organisation for Economic Co-
operation and Development (OECD), with
34 member countries across the globe, plus
the European Commission, have published
four volumes on the 'Safety assessment of
transgenic organisms'
(OECD, 2010), a
series of consensus documents for the work
on the 'Harmonisation of regulatory
oversight in biotechnology' (OECD, 2012a),
a series of consensus documents for the
work on the 'Safety of novel foods and feeds'
(OECD, 2012b) and three consensus
documents facilitating harmonization of the
'Work on the safety of novel foods and feeds'
(OECD, 2012c), of which the 'Considerations
for the safety assessment of animal
feedstuf s derived from genetically modii ed
plants' (OECD, 2003) specii cally addresses
the safety assessment of GM feed.
International treaties have also been put
forward to enhance trade. Trade problems
arise when countries have dif erent legal
requirements regarding the detection,
labelling and approval procedures necessary