Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
select transformed cells from a population
of non-transformed plant cells, or to
distinguish transgene-containing progeny
plants from the segregants without the
transgene (Fig. 2.2).
An example of the second category
is 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate syn -
thase (EPSPS). h is plant enzyme plays a
role in the biosynthesis of the aromatic
amino acids, phenylalanine, tyrosine and
tryptophan. h e herbicide, glyphosate, is a
competitive inhibitor of the endogenous
enzyme. However, a variant EPSPS present
in a special strain of
Agrobacteria
has a
slightly altered shape. h is alteration
prevents glyphosate from binding, thus
allowing the resistant EPSPS to catalyse the
amino acid synthesis reaction. In this way,
the expression of this gene in the transgenic
plant gives a competitive advantage to the
wild-type cells by bypassing the blocked
biosynthetic pathway route and restoring
the essential function.
h us, only plants that have integrated the
selectable marker gene will survive on tissue
culture media complemented with the
appropriate antibiotic or herbicide (see
Section 2.2.7).
Similar to the transgene construct of
interest, the selectable marker gene also
needs the appropriate promoter and
termination signals to allow functional
expression of this trait. Selectable marker
genes are driven mostly by promoters that
result in constitutive expression such as the
CaMV 35S and the nopaline synthase
promoter for transformation of dicotyledon-
ous plants and promoters of the ubiquitin
gene of maize and the actin gene of rice for
monocotyledonous plants.
Because antibiotics are used to combat
human and animal pathogens, special care
has been taken to study the spread of the
resistance genes from the transgenic plants
to the pathogens. Indeed, when the
pathogens acquire these same resistance
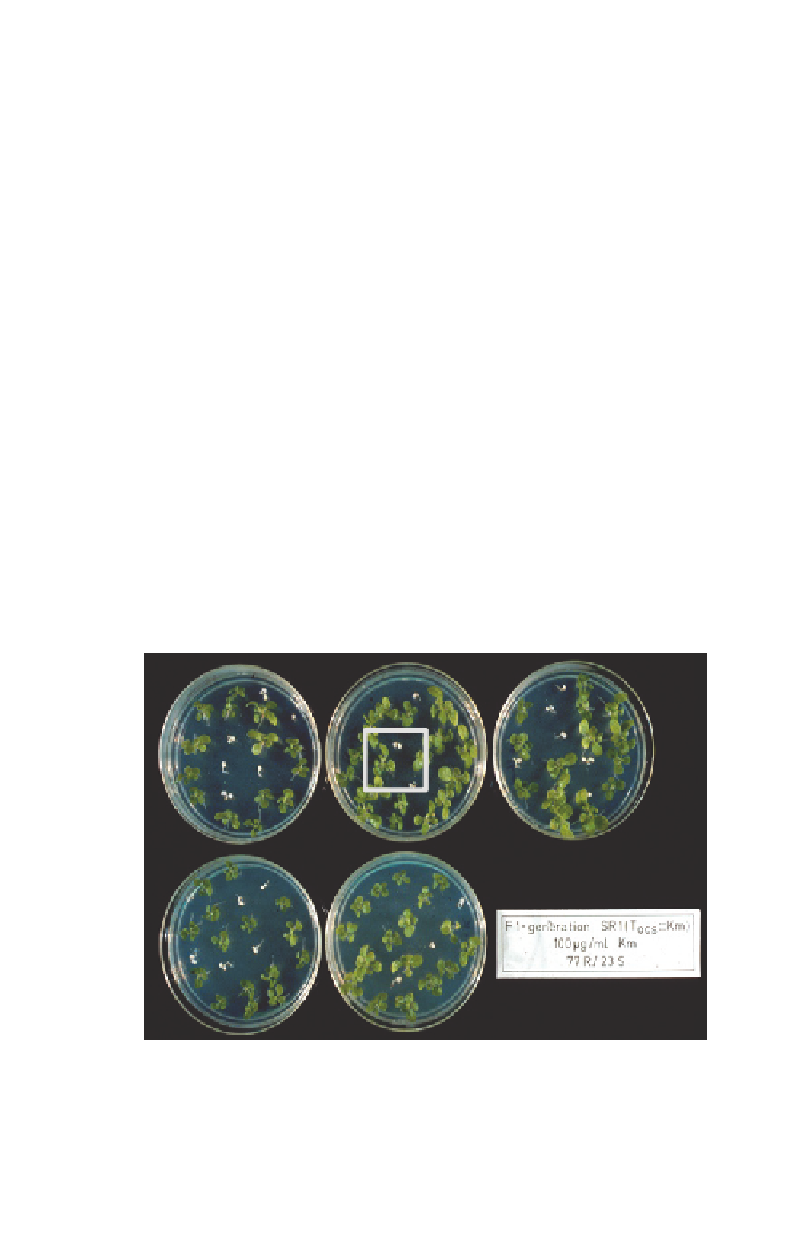
Fig. 2.2.
Use of selectable markers, such as
nptII
conferring resistance to the antibiotic kanamycin. The
progeny of a transformant segregate, the selectable marker and the transgene as a Mendelian marker in
a 3 to 1 ratio: large seedlings that contain the antibiotic-resistance marker are green, and can make new
leaves and roots; small seedlings that do not contain the selectable marker are sensitive to kanamycin,
stop photosynthesis and are white.