Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
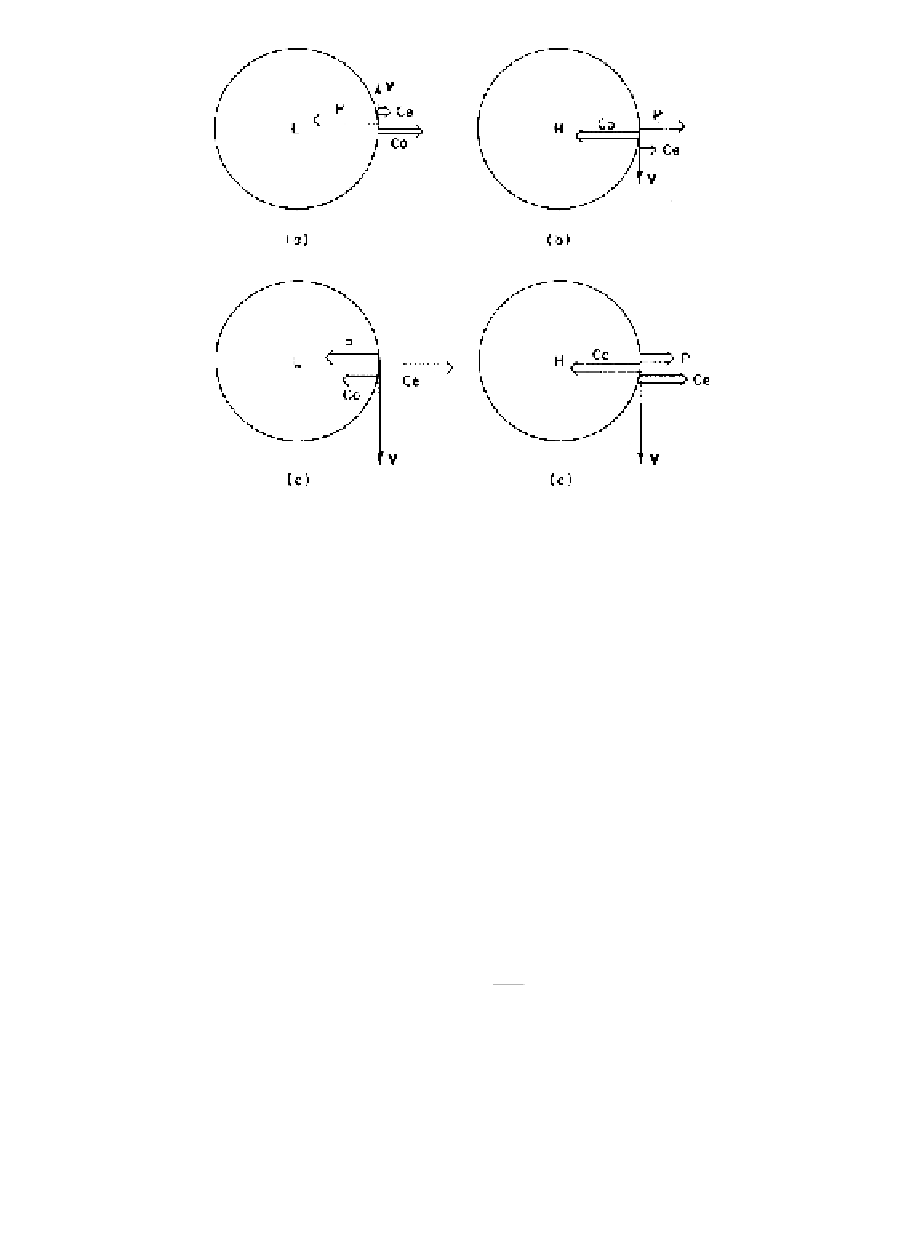
Fig. 3.5
Force balances in the Northern Hemisphere for the four types of gradient flow: (a) regular
low (b) regular high (c) anomalous low (d) anomalous high.
called
baric
. The anomalous low is antibaric; the geostrophic wind V
g
defined in
(3.11) is negative for an anomalous low and is clearly not a useful approximation to
the actual speed.
4
Furthermore, as shown in Fig. 3.5, gradient flow is cyclonic only
when the centrifugal force and the horizontal component of the Coriolis force have
the same sense (Rf > 0); it is anticyclonic when these forces have the opposite
sense (Rf < 0). Since the direction of anticyclonic and cyclonic flow is reversed
in the Southern Hemisphere, the requirement that Rf > 0 for cyclonic flow holds
regardless of the hemisphere considered.
The definition of the geostrophic wind (3.11) can be used to rewrite the force
balance normal to the direction of flow (3.10) in the form
V
2
/R
+
fV
−
fV
g
=
0
Dividing through by fV shows that the ratio of the geostrophic wind to the
gradient wind is
V
g
V
=
V
fR
1
+
(3.17)
For normal cyclonic flow (fR > 0), V
g
is larger than V , whereas for anticy-
clonic flow (fR < 0), V
g
is smaller than V . Therefore, the geostrophic wind is an
4
Remember that in the natural coordinate system the speed
V
is positive definite.