Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
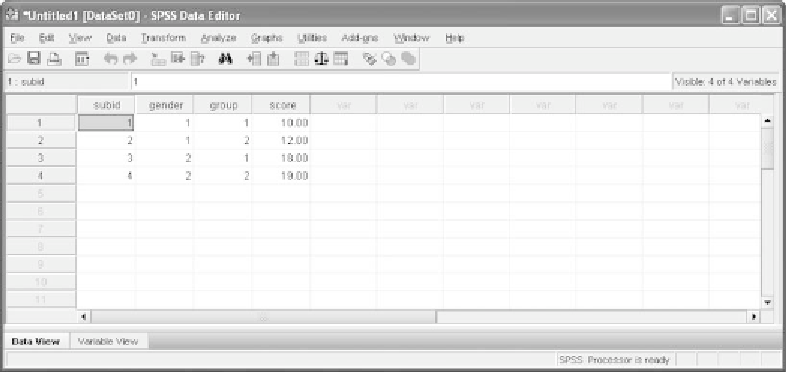
Figure A12
The data in the Excel file are now in an SPSS data file.
many lines of data (they are called
records
) for participants as you wish.
The important point to remember is that the document must be saved as a
text file (it has the extension
.txt
). A text file is one that contains just ordi-
nary characters (e.g., digits, letters) and some control characters (e.g.,
tabs, carriage returns) but does not contain formatting information
(e.g., bold or italic font, subscripts and superscripts).
To create a text file, you can type your data directly into Notepad
(in Windows) or TextEdit (on a Mac) and save the file automatically as
a text file; alternatively, you can type your data into a word processing
application such as Microsoft Word and use the
Save As
option on its
File
menu to save the document as a text file. We show a portion of a text
document in Figure A13. Each participant (case) in this example occupies
twenty-seven lines of data.
To bring the contents of a text file into an SPSS data file format, you
must open the file through SPSS. Here is one way to do this. From the
main SPSS menu select
File
➜
ReadTextData
.Thiswillopenanavigation
window where you can select which text file you want SPSS to transform
to a data file. Once you select a file by highlighting its name and clicking
Open
, you will be brought to the
Te x t Impo r t Wi z a rd
window, which
will take you step by step through the six-step process of bringing the
contents of a text file into SPSS. Here is a brief description of the six
steps.
A.10.1 STEP 1
Step 1 is contained in the first dialog window you see in
Te x t Impo r t
Wizard
; it is shown in Figure A14.1. You can see the first five rows of
text in the bottom panel; this is a quick way to verify that you have
retrieved the right file. If you have not previously set up a defined format