Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
H
H
y
H
x
=
−
=
arg
P
H
.
In the
t
-domain
E
x
(
t
)
E
y
(
t
)
|
E
x
E
x
|
−
cos (
t
)
E
τ
(
t
)
=
=
,
y
)
|
E
y
|
cos (
t
−
(2
.
10)
H
x
(
t
)
H
y
(
t
)
|
H
x
|
x
)
cos (
t
−
=
=
.
H
τ
(
t
)
H
y
)
|
H
y
|
cos (
t
−
t
from (2.10), we obtain the equations for the
ellipses described by the endpoint of the vectors
E
τ
(
t
),
H
τ
(
t
):
Eliminating sin
t
and cos
E
y
(
t
)
|
E
y
|
E
x
(
t
)
|
E
x
|
E
x
(
t
)
E
y
(
t
)
|
E
x
||
E
y
|
E
sin
2
E
+
−
2cos
=
,
2
2
(2
.
11)
H
y
(
t
)
|
H
y
|
H
x
(
t
)
|
H
x
|
H
H
x
(
t
)
H
y
(
t
)
|
H
x
||
H
y
|
sin
2
H
+
−
2cos
=
.
2
2
These ellipses received the name
polarization ellipses.
Parameters of the polariza-
tion ellipses can be defined through the polarization ratios.
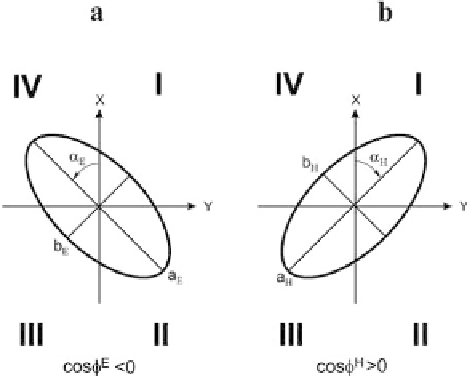
Let us begin with the polarization ellipse for the electric field (Fig. 2.1a). First
find the angle
E
made by the major axis of the polariz
ation ellipse wi
th the
x
-axis.
To this end, determine the time
t
o
, at which
E
τ
E
x
(
t
)
(
t
)
=
+
E
y
(
t
) is maximum.
From the conditions
Fig. 2.1
Polarization ellipses
of electric (
a
) and magnetic
(
b
) eigenfields.
I
,
II
,
III
,
IV
-
numbers of quadrants