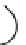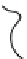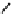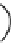Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
3D
1D
2D
a
b
x
x
x
y
y
y
x
x
x
x
y
y
y
y
x
x
x
x
y
y
y
y
Fig. 1.7
Polar diagrams of the impedance tensor
1D:
Z
=
4
−
2
i
04
−
2
i
ske
w
=
0
S
2D: [
Z
]
=
,
−
1
+
2
i
0
ske
w
=
0
B
−
0
.
5
−
3
i
4
−
2
i
ske
w
=
0
S
3D:
a)
[
Z
]
=
,
−
1
+
2
i
0
.
5
−
3
i
ske
w
=
0
.
47
B
−
0
.
5
−
3
i
4
−
2
i
−
ske
w
S
=
0
.
63
ske
w
B
=
b)
[
Z
]
=
,
+
.
−
i
.
1
2
i
0
1
0
44
Consider the 2D-model (
ske
w
=
0
,
ske
w
=
0) striking along the
x
-axis.
S
B
According to (1.49) and (1.87),
|=
Z
−
Z
⊥
sin
,
|
Z
xx
(
)
cos
Z
cos
2
,
Z
⊥
sin
2
|
Z
xy
(
)
|=
+
(1
.
88)
,
arg
Z
xy
(
)
=
arctan
Im (
Z
cos
2
Z
⊥
sin
2
+
)
Z
⊥
sin
2
Re (
Z
cos
2
+
)
where
Z
and
Z
⊥
are the longitudinal and transverse impedances. The diagram of
|
Z
xx
|
looks like a flower with four identical petals. The lines bisecting the angles