Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
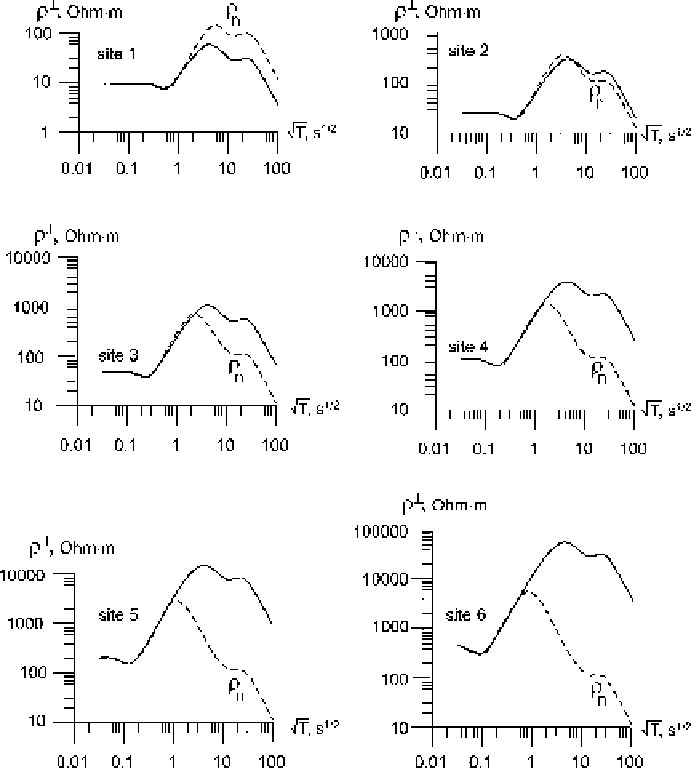
Fig. 11.2
Transverse apparent-resistivity curves in the model of the
S-
effect from Fig. 11.1
⊥
-curves diverge within a range of the slightly distorted
high-frequency branches of the
Fig. 11.5. The adjacent
⊥
-curves, but they come together within a range of
the statically shifted low-frequency branches of these curves. So, the initial period
T
s
of the
S
-effect can be evaluated as a boundary between zones with diverged and
converged phase curves. Using this indication in the case under consideration, we
get
T
s
≈
9s.
Now consider the
effect. The case is illustrated in Fig. 11.6. Here the upper
layer contains a two-dimensional small outcropped inclusion, 10 m thick and 120 m
wide, consisting of conductive and resistive sections, while the host medium is the
same as in the previous model given in Fig. 11.1. The transverse
−
⊥
-curves are
presented in Fig. 11.7. They show the conspicuous static shift, though variations