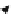Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
start from the Maxwell equations and construct a model with a functionally deter-
ministic magnetotelluric impedance tensor.
Let a plane elliptically polarized monochromatic wave with the components
E
x
,
E
y
and
H
x
,
H
y
be incident vertically on the Earth's surface
z
=
0 (Fig. 1.1) The
air is an ideal insulator. The Earth with magnetic permittivity
o
of vacuum con-
sists of horizontally homogeneous isotropic layers with normal conductivity
N
(
z
)
and contains a bounded inhomogeneous domain V with excess electric conductiv-
ity
(
x
,
y
,
z
)
=
(
x
,
y
,
z
)
−
N
(
z
)
.
The problem is solved in a quasi-stationary
approximation.
The electromagnetic field within the Earth meets the equations
curl
H
=
E
=
N
E
+
j
(1
.
4)
curl
E
=
i
o
H
,
where
j
=
E
is the density of excess currents distributed within inhomogeneous
domain V.
We will represent
E
H
as the sum of the normal field
E
N
H
N
, and the anomalous
,
,
field
E
A
H
A
:
,
E
N
E
A
H
N
H
A
E
=
+
,
H
=
+
.
0) is a horizontally uniform field
observed within the host Earth in the absence of the inhomogeneities. It satisfies the
equations
The
normal field
E
N
(
E
x
,
E
y
,
0),
H
N
(
H
x
,
H
y
,
curl
H
N
=
N
E
N
,
(1
.
5)
curl
E
N
o
H
N
=
i
.
E
x
, H
x
E
y
, H
y
x
air
earth
y
σ
N
µ
0
z
V
σ
N
+
Δσ
Fig. 1.1
A layered model
with an inhomogeneous
three-dimensional domain
V