Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
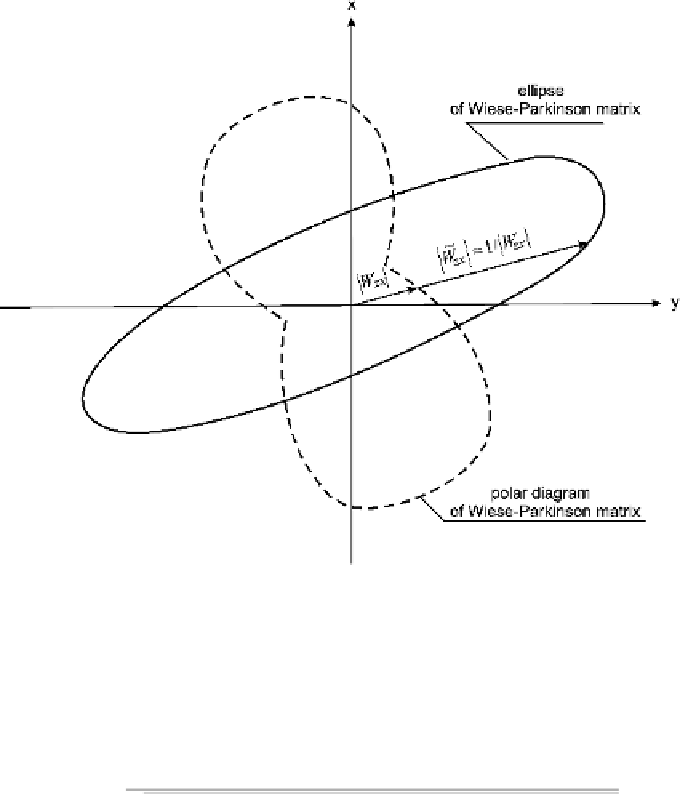
Fig. 4.7
The Wiese-Parkinson polar diagram and ellipse
It is notable that an inversion of the polar diagram of the Wiese-Parkinson matrix
gives an ellipse (Fig. 4.7). Its equation is
W
zx
(
)
=
1
,
(4
.
37)
+
W
zy
2
sin
2
W
zy
sin
2
cos
2
|
W
zx
|
+
2Re
W
zx
cos
where
)
=
W
zx
(
|
.
Let us compare equations (4.34) and (4.25). The directions of the major and
the minor axes of the polar diagram of the Wiese-Parkinson matrix coincide with
directions of the quasi-transverse and quasi-longitudinal magnetic fields defined by
the Vozoff technique. Thus, with (4.26) we can choose the major semi-axis of polar
diagram, which points away from zone of higher conductivity and toward zone of
lower conductivity (the Wiese convention).
Examples of polar diagrams of the Wiese-Parkinson matrix for 2D and 3D-
models are shown in Fig. 4.2. The polar-diagram major semi-axes which satisfy
condition (4.26) are indicated by arrow. They are parallel to the Vozoff tippers V
and point away from zone of higher conductivity.
1
/
|
W
zx
(
)