Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
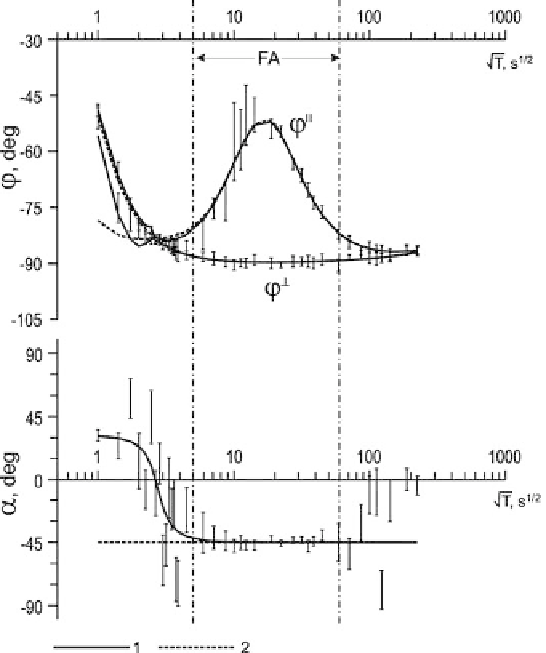
Fig. 3.7
The Bahr decomposition in the superimposition model shown in Fig. 1.11;
-regional
⊥
- longitudinal and transverse phases of the two-dimensional regional impedance;
vertical bars characterize the data scattering caused by measurement noise, FA - favorable area,
1-data for the noise-free impedance, 2-true data
and
strike,
decomposition. To this end we analyze
skew
S
and
skew
B
as well as phase param-
eter
. In the later stage we take better advantage of
Groom-Bailey's least squares fitting procedure and find regional strike angle
and phase difference
R
,
R
R
2
regional impedance phases arg
1
,
arg
as well as twist and shear angles
t
,
s
. These latter can be converted to Bahr's deflection angles
x
,
y
which offer
a clearer view of near-surface inhomogeneities. And finally the slight frequency
dependence of
1
2
, and
R
,arg
,
arg
t
,
s
may serve as a criterion for reliability
of the local-regionall decomposition.
Following Jones and Groom (1993) and McNeice and Jones (2001), we can
increase the noise-immunity of the Bahr-Groom-Bailey decomposition and separate
the local and regional effects even in the case that the phase difference between the
longitudinal and transverse regional impedances is rather small. On this way we
apply the least squares statistic to a band of
n
frequencies and compose a system of