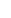Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
1
7
11
PLAN
x
2
8
8
12
12
y
ρ
A
,
Ohm.m
6
êì
6 km
3
5
5
9
9
13
T
=
640 s
4
610
6 km
610
14
100
ρ
ρ
10 Ohm.m
100 Ohm.m
100 Ohm m
×
10
1
10
100
T, s
1/2
5
5
Ohm.m
arg
Z
-15
-30
-45
-60
T = 640 s
200
km
arg
Z
10000
Ohm.m
arg Z, deg
1
Ohm.m
CROSS-SECTION
Fig. 2.3
A superimposition model with a
-shaped near-surface resistive inclusion and a 2D deep
regional conductive prism; (
a)
the plan and cross-section of the model, 1, 2, 3,
observation
sites, (
b)
the longitudinal and transverse apparent-resistivity and impedance-phase curves over the
middle of the regional prism in the absence of the near-surface inclusion
...
scatter caused by local distorting influence of the near-surface
-shaped inclusion,
,
⊥
while arg
1
,
arg
2
are close to arg
arg
obtained in the absence of the near-
surface inclusion.
Similarly, we compare the principal directions,
2
, of the impedance ten-
sor [
Z
] defined by all three methods. Here the more variegated pattern is observed
(Fig. 2.5). Though the
1
and
-values obtained by different techniques are in good qualita-
tive agreement, the difference between them is at some sites about 15-25
◦
. The SE
and LMK methods yield the best correlated
2
-values
are given by the SSB and LMK methods. Note that deviation of principal directions
of the superimposition impedance tensor from principal directions of the regional
two-dimensional impedance tensor ranges up to about 40
◦
, but this scatter can be
readily removed by averaging.
Distinction between the different eigenstate techniques vividly manifests itself
in the inhomogeneity parameter
N
calculated by (2.53) as well as in the angular
and elliptical parameters of asymmetry,
ske
1
-values. The best correlated
w
pol
, calculated by (2.54),
(2.55). Figure 2.6 shows these parameters in comparison with the asymmetry param-
eter
ske
w
ang
and
ske
S
. Recall that deviation of
N
from zero reflects the lateral effects caused
by 2D or 3D structures, while deviation of
ske
w
S
from zero
points to the 3D asymmetry. In the model under consideration all eigenstate tech-
niques give the same qualitative pattern for
w
ang
,
ske
w
pol
and
ske
w
w
pol
, but it is
remarkable that the LMK method offers the maximum
N
-values being the most
|
|
,
w
ang
N
ske
and
ske