Java Reference
In-Depth Information
The cache is used by the central processing unit (CPU) to reduce the average
access time to instructions and data. The cache is a small, fast memory that stores
the contents of the most frequently used main memory locations. Contemporary
CPUs include an instruction cache to speed up the fetching of executable instruc-
tions and a data cache to speed up the fetching and storing of data.
The most common secondary storage devices are
hard disks
and USB
flash
drives
. A typical USB flash drive stores between 1 GB and 256 GB of information.
The storage capacities of hard drives vary, but on personal computers, capacities
typically range between 120 GB and 500 GB, such as in the system described in
Figure 1.8. Some hard disks can store 2 TB of data.
A USB flash drive consists of a small printed circuit board carrying the circuit
elements and a USB connector, insulated electrically and protected inside a plastic,
metal, or rubberized case, which can be carried in a pocket or on a key chain, for
example.
A disk is a magnetic medium on which bits are represented as magnetized parti-
cles. A read/write head passes over the spinning disk, reading or writing information
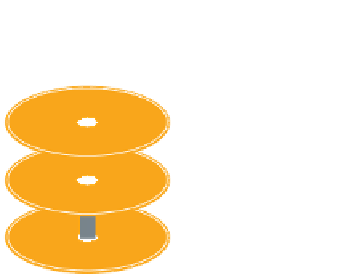
as appropriate. A hard disk drive might actually contain several disks in a vertical
column with several read/write heads, such as the one shown in Figure 1.12.
To get an intuitive feel for how much information these devices can store,
consider that all the information in this topic, including pictures and formatting,
requires about 7 MB of storage.
Magnetic tapes
also have been used as secondary storage but are considerably
slower than hard disk and USB flash drives because of the way information is
accessed. A hard disk is a
direct access device
since the read/write head can move, in
general, directly to the information needed. A USB flash drive is also a direct access
Read/write
head
Disks
FIGURE 1.12
A hard disk drive with multiple disks and read/write heads












Search WWH ::

Custom Search