Game Development Reference
In-Depth Information
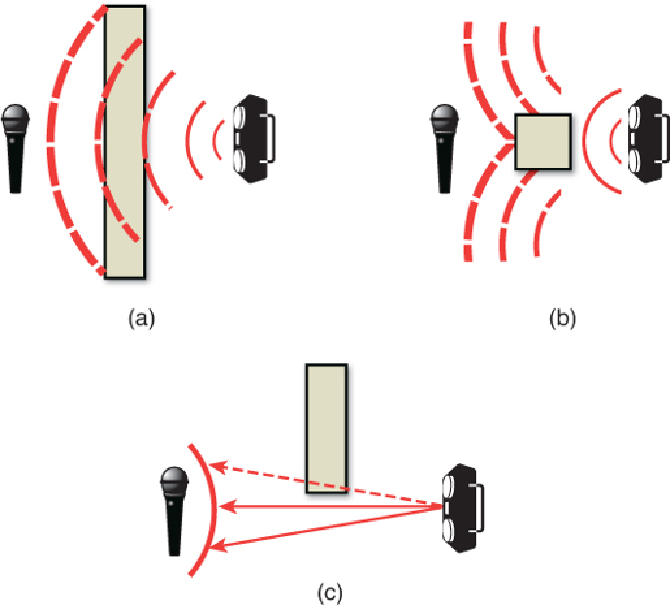
Figure 6.7
Sound occlusion (a), sound obstruction (b), and Fresnel acoustic dif-
fraction (c).
Sound occlusion occurs when sound does not have a direct path from emitter to
listener, but rather must travel through some material to reach the listener. The
predominant result of sound occlusion is that a low-pass filtering occurs, which
means the volume of higher frequency sounds is reduced. That's because lower
frequency waves have an easier time passing through surfaces than higher fre-
quency ones. However, another outcome of sound occlusion is an overall reduc-
tion in volume levels of all the sounds.
Similar but different is the idea of
sound obstruction
(also known as diffraction).
With sound obstruction, the sound may not have a straight line path, but is able to
travel around the obstacle, as shown in
Figure 6.7(b)
.
For example, if you yell at