Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
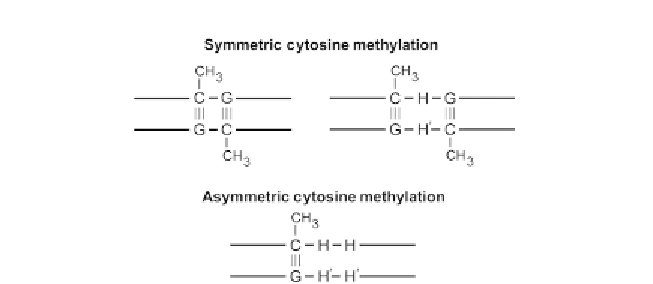
Figure 1.1 Schematic of symmetric and asymmetric sites of cytosine methylation in
higher eukaryotic species. CpG and CpHpG are symmetric sites of DNA methylation,
and CpHpH is an asymmetric site of methylation. H is adenine, thymine, or cytosine.
H
0
is the base paired to H.
cytosine bases undergo direct covalent modifications to produce 5-hmC
(
Wu and Zhang, 2010
). (Possible roles of hydroxymethylcytosine and
related modifications will be discussed in
Section 5
.) Eukaryotic cytosine
methylation occurs in two distinct sequence contexts (
Fig. 1.1
). Symmetric
cytosine methylation, in which cytosines on opposite strands of DNA are
methylated, is found in both plants and animals. For example, in the
commonly studied angiosperm, the mustard
Arabidopsis thaliana
, symmetric
cytosine methylation is found on numerous 5
0
-CpG-3
0
dinucleotide and
5
0
-CpHpG-3
0
trinucleotide sites, where H is adenine (A), thymine (T),
or cytosine (C), that is on any base except guanine (
Cokus et al., 2008;
Goll and Bestor, 2005
). Among animals, mammalian species particularly
human and mouse have informed us most about cytosine methylation. With
the exception of non-CpG methylation, which is known to exist at a very
low level in specific cell types, such as postmitotic germ cells and cultured
induced pluripotent stem and embryonic stem (ES) cells (
Arand et al., 2012;
Ichiyanagi et al., 2013; Ramsahoye et al., 2000
), cytosine methylation is
symmetric and confined to 5
0
-CpG-3
0
dinucleotides. Asymmetric methyl-
ation is present in
A. thaliana
and is found in 5
0
-CpHpH-3
0
trinucleotides
(
Cokus et al., 2008
). With the constraints of Watson-Crick base-pairing
rules, this type of methylation is confined to the single cytosine base among
the six nucleotides of the base-paired triplet, hence the term asymmetric
methylation. It is not confined, however, to just a single strand of the double
helix—both complementary single strands can contain asymmetrically
methylated cytosines, albeit on unrelated sequences.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search