Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
details are not yet known, for example, the role of the different CRCs and
which cargo proteins ride with one and the same vesicle, which ones are
Golgi-derived, and which membrane proteins are delivered by free ribo-
somes. Input by endocytotic components is well founded up to now mostly
in
Dictyostelium
. Evidence comes from the presence of adaptor proteins and,
also in
Dictyostelium,
smaller vesicles fusing to a big CV are considered of
endocytotic origin (
Macro et al., 2012; Zanchi et al., 2010
). Differences
in the endocytotic input may exist between the different systems.
Microtubule bundles associated with the fully developed CVC serve for
reinforcement, rather than as trafficking rails since they are surrounded by
the densely packed spongiome. These microtubules may require the post-
translational modifications reported (
Section 5.1
) to achieve stability and
interaction with motor proteins. Among them are myosins and dyneins,
but kinesins also have to be expected.
Not only silencing of SNAREs reduces the spongiome in the
Paramecium
CVC, as shown by
Sch
¨
nemann et al. (2013)
for Syx2 and in
Fig. 9.3
for
Syb2, but also silencing of
Pt
CRC-II/InsP
3
R(
Fig. 9.4
). Also simultaneous
silencing of H
þ
-ATPase SUs c2, c4, and c6 (in experimental series described
by
Wassmer et al., 2006
) results in similar changes in ultrastructure. This
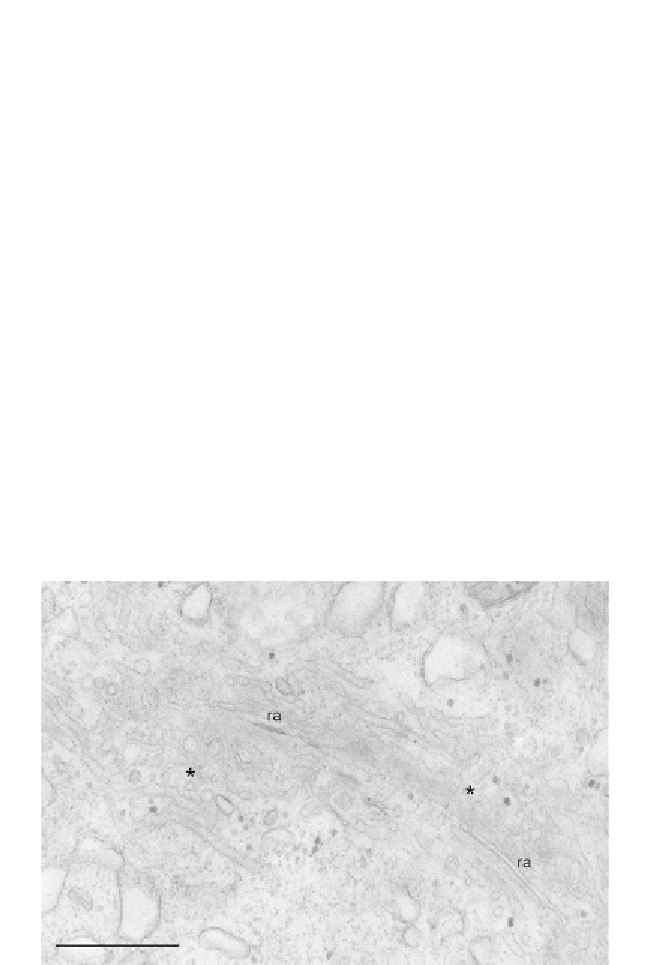
Figure 9.3 Degradation of CVC ultrastructure in P. tetraurelia after silencing of Syb2. To
be compared with the control presented in
Fig. 9.2
. The radial arm (ra) is collapsed and
only vestigial remnants of the smooth and decorated spongiome are left (asterisks).
Bar
0.1 mm. Unpublished micrograph from experimental series described by
Schilde
et al. (2006)
.
¼
Search WWH ::

Custom Search