Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
k
ρ
k
!
P
=
(4)
k
2
k
ρ
ρ
1
++ ++
ρ
...
2
k
!
⎛⎞
λ
μ
(
)
Ln P
=
1
−
The average number of port
,The probability of system full
⎜
⎝⎠
s
n
P
the probability that port has free users and can connect to the Internet
is
P
is the probability that a user is rejected.
PP
=−
1
when
kn
=
is
, and then
n
Table 1.
Queuing model tables
1/
μ
λ
/
μ
1
P
L
P
1
9.375
0.0146671
0.985323
9.2375
1.5
14.0625
0.116352
0.883648
12.4263
2
18.75
0.257403
0.742597
13.9237
3
28.125
0.467174
0.532826
14.9857
4
37.5
0.590668
0.409332
15.35
5
46.875
0.668793
0.331207
15.5253
In theory, as long as the number of users in the system does not exceed capacity
limit, for any user number k, users can't feel reception available resources reduce. We
believe that the average service rate of each desk is the same
, and the user's Internet
time obeys the negative exponential distribution parameter. However, in real network
systems, because information is transmitted by packets, different user data pack will
constantly collide. In the case of the system's hardware resources is limited, when the
number of user k increases to a degree, users can obviously felt the efficiency of sys-
tem service decrease, it will affect the user's mental state, thus affecting their Internet
time. Therefore, when the system is to have multiple users, each at the reception desk
for an average service rate although same
μ
μ
, and its distribution
is not negative exponential distribution, will become the general distribution. Showed
by
, but with less than
μ
n
M Gnn
/
///
∞
, this service system's structure as shown in the diagram.
M Gnn
/
///
∞
Fig. 2.
system state probability distribution and state transfer speed
diagram
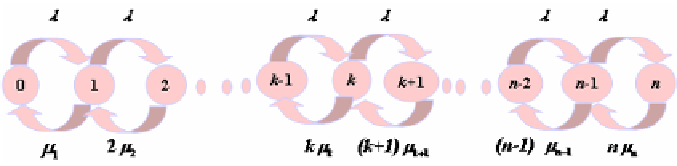
















Search WWH ::

Custom Search