Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
administrator to reconfigure the system easily so as to parcel out the resources to
meet changing workload demands. Domain configurations can be optimized for
workloads that are either compute intensive, I/O intensive, or both. DR can also
be used to remove and replace failed or upgraded hardware components while the
system is online. This flexible resource allocation technology is critical in ensuring
a robust virtualization solution.
The DR functions of Sun SPARC Enterprise M-Series servers are performed
on XSB units and managed through the XSCF. The XSCF security management
restricts DR operations to administrators who have the proper access privileges.
For example, on Sun SPARC Enterprise M8000 and M9000 servers, an IT opera-
tor can first use DR to delete a faulty system board and then use the system's
hot-plug feature to physically remove it. After plugging in the repaired board or
a replacement, DR can be used to add the board into the domain. In addition,
combining the capabilities of DR with network and storage multipathing solutions
can foster creation of redundant network or storage subsystems with automatic
failover, load balancing, and dynamic reconfiguring capabilities.
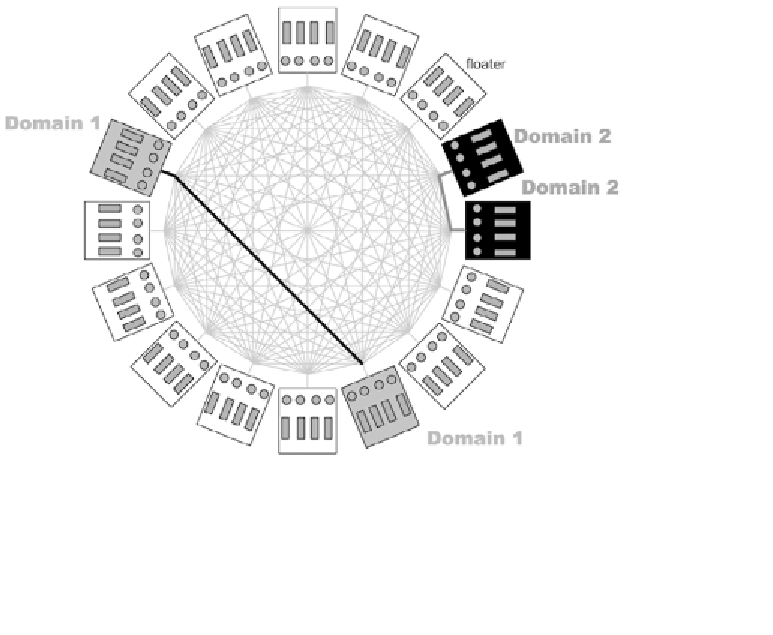
Figure 2.14 provides an example of DR carried out on a system board for an
M9000. In this figure, the floater XSB can be assigned to either Domain 1 or
Domain 2. This XSB has 4 CPUs, 32 memory DIMMs, and an optional 8 PCIe
Figure 2.14
Two Domains on M9000-64
Search WWH ::

Custom Search