Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
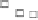
The night-time replenishment of ozone is caused by entrainment of
ozone from the free troposphere into the boundary layer. The over-
night loss of peroxide is due to deposition over the sea surface (and
heterogeneous loss to the aerosol surface), as peroxide has a signif-
icant physical loss rate, in contrast to ozone which does not. There-
fore, the daytime anti-correlation of ozone and peroxide is indicative
of the net photochemical destruction of ozone.
2.5.3 Role of Hydrocarbons
The discussion up to this point has focused in the main on the role of CO
and CH
4
as the fuels for atmospheric oxidation. It is clear that there are
many more carbon compounds in the atmosphere than just these two.
21
One of the roles of atmospheric photochemistry is to ''cleanse'' the
troposphere of a wide-range of these compounds. Table 3 illustrates the
global turnover of a range of trace gases including hydrocarbons and
illustrates, for a number of trace gases, the primary role played by OH in
their removal. NMHC have a range of both biogenic and anthropogenic
sources.
5,21
Carbon monoxide chemistry is not independent from
NMHC chemistry as 40-60% of surface CO levels over the continents,
slightly less over the oceans, and 30-60% of CO levels in the free
troposphere, are estimated to come from NMHC oxidation.
22
15.0
1,100
14.8
1,000
14.6
14.4
900
14.2
14.0
800
13.8
700
13.6
13.4
600
13.2
500
13.0
1
6
12
18
21
Hour of day
Figure 14 Average diurnal cycles for peroxide (open squares) and ozone (filled squares)
in baseline air at Cape Grim, Tasmania (411S) for January 1992
20