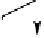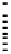Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
O
3
+ h
ν
OH
H
2
O
+
CH
4
CH
3
+ O
2
CH
3
O
2
NO
HO
2
O
3
h
ν
+ O
2
CH
3
O
CH
3
OOH
NO
2
+ O
2
O
3
NO
HO
2
O
3
h
ν
+ O
2
h
ν
NO
2
O
2
OH
HCHO
h
ν
CO(+2HO
2
)
CO
2
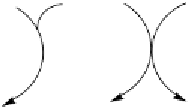
Figure 10 Simplified mechanism for the photochemical oxidation of CH
4
in the troposphere
62
The resulting methoxy radical reacts rapidly with O
2
to form formalde-
hyde and HO
2
.
CH
3
O
þ
O
2
-
HCHO
þ
HO
2
(2.22)
The oxidation of methane is summarised schematically in Figure 10. The
OH radical may have another fate, dependant on the concentration of
NO
2
, it can react with NO
2
to form nitric acid.
OH
þ
NO
2
þ
M
-
HNO
3
þ
M
(2.23)
The formation of HNO
3
represents an effective loss mechanism for both
HO
x
and NO
x
.