Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 3 Structures of common primary soil minerals
Quartz
SiO
2
Feldspars
Microcline
KAlSi
3
O
8
Albite
NaAlSi
3
O
8
Anorthite
CaAlSi
2
O
8
Micas
Muscovite
KAl
2
(Si
3
Al)O
10
(OH)
2
Biotite
K(Mg, Fe)
2
(Si
3
Al)O
10
(OH)
2
Amphiboles
Hornblende
(Na, Ca)
2
(Mg, Fe, Al)
5
(Si, Al)
8
O
22
(OH)
2
Pyroxenes
Enstatite
MgSiO
3
Augite
Ca(Mg, Fe, Al)(Si, Al)
2
O
6
Olivine
(Mg, Fe)
2
SiO
4
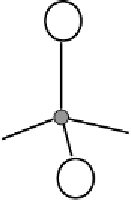
(a)
(b)
Silicon
Aluminium
Oxygen or hydroxyl
Figure 3 Structure of (a) silica tetrahedron and (b) alumina octahedron
(Figure 4). Quartz and the feldspars are framework silicates, in which
adjacent tetrahedra share all four oxygens. The micas form sheet silicates
by the sharing of three oxygens by each silica tetrahedron. The amphi-
boles and pyroxenes are chain silicates: amphiboles are double chains,
with the tetrahedra sharing two or three oxygens alternately; pyroxenes
are single chains with sharing of two oxygens. Olivine is an isolated
tetrahedon (or orthosilicate).