Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
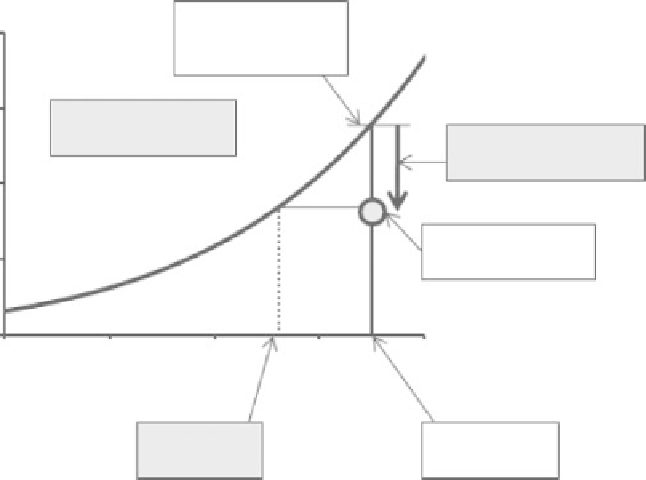
Saturated vapor
pressure at air
temperature (
e
sat
)
8
6
Relative humidity
RH
= (
e
/
e
sat
) x 100%
Vapor pressure deficit
D
= (
e
sat
-e
)
4
Vapor pressure
of the air (
e
)
2
0
0
10
20
T
C
C
30
40
Figure 2.3
Measures of the
extent of atmospheric saturation
and temperatures used when
measuring the vapor pressure of
moist air.
“Dew point”
temperature
Air
temperature
(
)
Dee
=−
(2.20)
sat
Knowing the value of
D
for air is particularly important when calculating
evaporation rate because it provides a direct measure of how much additional
water vapor the atmosphere can hold.
Measuring the vapor pressure of air
The
dew point
of air,
T
dew
(see Fig. 2.3) is a measure of the vapor pressure of the air.
Dew point is defined as the temperature to which air must be cooled at constant
pressure for it to saturate. It can be shown by inverting Equation (2.17) that for air
with vapor pressure
e
(in kPa), the dew point of the air in
°
C is given by:
()
ln
e
+
0.49299
T
=
(2.21)
()
dew
0.0707
−
0.00421 ln
e
A
dew point hygrometer
measures the humidity of air by cooling an initially clear
mirror until its surface becomes clouded by water condensing onto the mirror.
The measured temperature of the mirror when this first occurs is the dew point
temperature of the air and the vapor pressure of the air (which is, by definition,
equal to the saturated vapor pressure at dew point) can be then calculated using
Equation (2.17).