Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
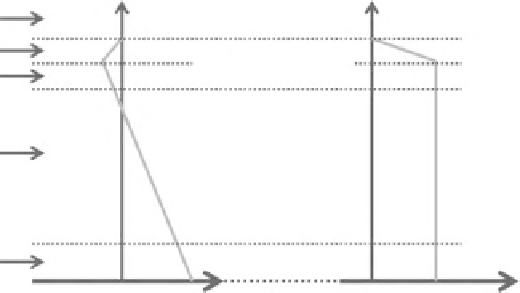
Free atmosphere
(v)
(iv)
(iii)
Entrainment layer
Figure 26.4
The simplified
average height dependence of the
sensible heat flux
H
(
z
) and the
moisture flux
E
(
z
) through the
daytime atmospheric boundary
layer over uniform terrain in
cloudless conditions when there
is no subsidence.
(ii)
Mixed layer
(i)
Surface layer
H
(
z
)
E
(
z
)
(j) How will the temperature and humidity change at level (i)?
(k) How will the temperature and humidity change at level (ii)?
(l) How will the temperature and humidity change at level (iii)?
(m) How will the temperature and humidity change at level (iv)?
(n) How will the temperature and humidity change at level (v)?
Question 9
(Uses understanding and equations
from Chapters 2, 21, 22 and 24.)
The molecular diffusion coefficients are
= 1.33 × 10
−5
(1+0.007
T
) m
2
s
−1
,
D
H
= 1.89 × 10
−5
(1+0.007
T
) m
2
s
−1
,
D
V
= 2.12 × 10
−5
(1+0.007
T
) m
2
s
−1
, and
D
C
=
1.29 × 10
−5
(1+0.007
T
) m
2
s
−1
, see Chapter 21.
Assume that the aerodynamic interactions of the leaves on deciduous trees can
be approximated by those of a circular flat plate with a diameter of 5 cm while
those of evergreen conifers can be represented by the aerodynamic interactions of
cylinders of diameter 2.5 mm. The boundary-layer resistance to heat transfer per
unit surface area of each vegetation element (i.e., leaf or needle) is estimated by
Equation (21.9). The in-canopy wind speed,
U
, is 0.5 m s
−1
and the in-canopy
temperature is 20°C. By first calculating the
Reynolds number
from
Re = (Ud)/
n
,
where
d
is a characteristic dimension of the leaf or needle (in this case the
diameter), and then by selecting the relevant empirical equation for the Nusselt
number,
Nu
, from Table (21.1), use Equation (21.9) to estimate the boundary-
layer resistance per unit area for heat transfer for:
υ
(a) individual deciduous leaves
(b) individual coniferous needles
Assume the transfer from individual vegetative elements is always by forced con-
vection so that the relative transfer resistances for other exchanges is determined