Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
u
(
t
)
Turbulent
fluctuation
Mean flow
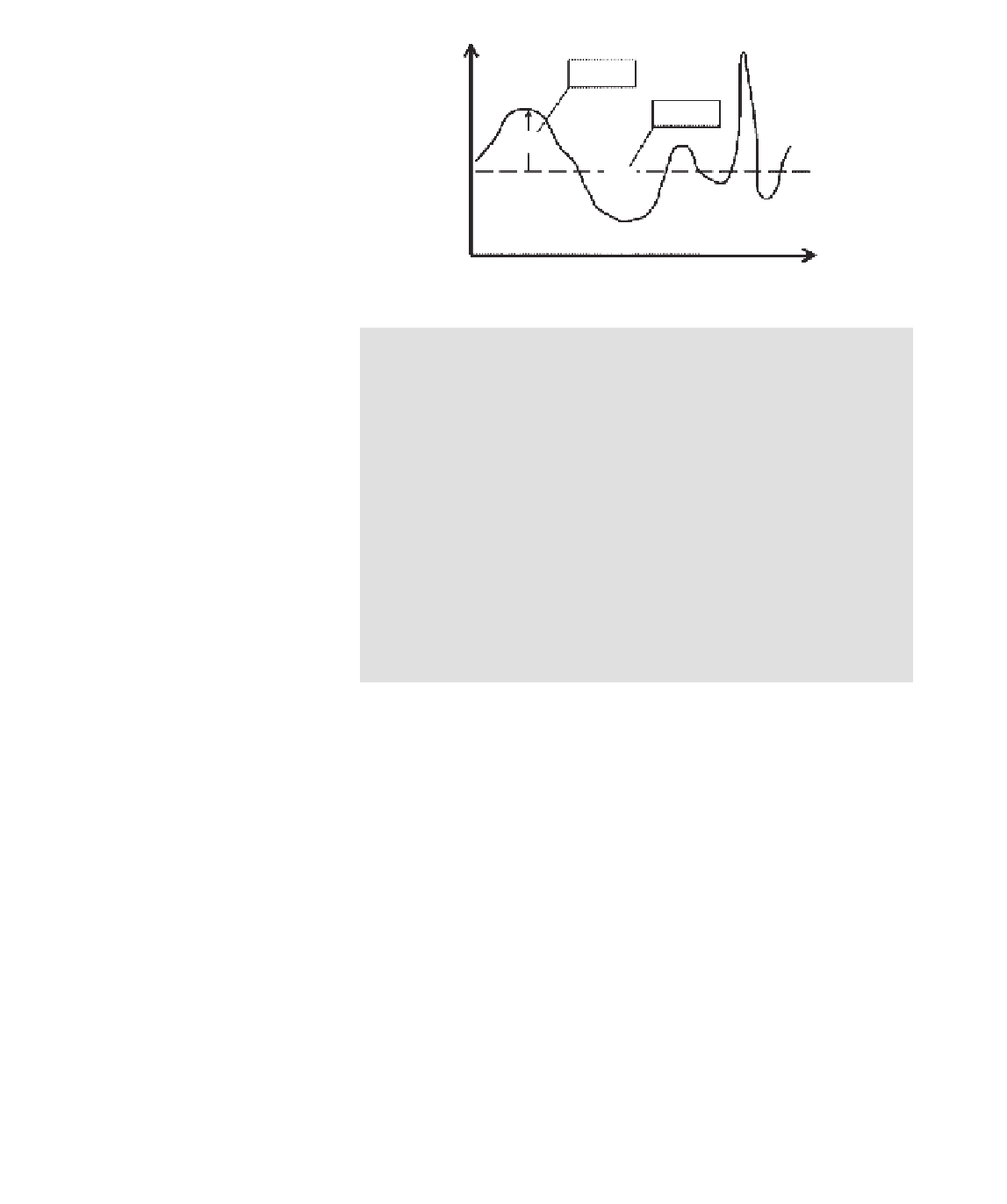
Figure 15.4
Separation of
the time dependent
horizontal wind speed along
the X axis,
u(t)
, into a time
dependent turbulent
fluctuation component,
u
′
(t)
, and a mean flow
component,
-
.
u
(
t
)
u
Time
Table 15.1
Atmospheric variables and their decomposition into components
representing the mean value of the variable and the fluctuating component
associated with turbulence.
Variable
Symbol and decomposition into
components
-
+
u
′
(
t
)
Wind speed parallel to the ground, along
direction of the mean wind
u
(
t
)
=
-
+
v
′
Wind speed parallel to the ground,
perpendicular to the direction of the mean wind
v
(
t
)
=
(
t
)
-
+
w
′
Wind speed perpendicular to the ground
w
(
t
)
=
(
t
)
-
+
q
v
′
Virtual potential temperature
q
v
(
t
)
=
(
t
)
-
+
q
′
Specific humidity
q
(
t
)
=
(
t
)
c
-
+
c
′
Atmospheric constituent, e.g. CO
2
c
(
t
)
=
(
t
)
variations that are superimposed on better described variation in their mean
values. Figure 15.4 illustrates this separation for the case of the wind speed
component,
u
, along the X axis selected to be parallel to the ground. All atmos-
pheric entities show similar variability in a turbulent field and can be similarly
re-written with separate mean and fluctuating components, see Table 15.1.
Rules of averaging for decomposed variables
It is useful that over a time period
T
of around 20-60 minutes all atmospheric
variables can be considered as being made up of the mean value over that period
and a fluctuating component which by definition has an average value of zero
when averaged over the period
T
. This allows simplifications when deriving
equations. Table 15.2 documents some of the more important mathematical results