Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
0.25
0.20
Solar irradiation curve outside atmosphere
Solar irradiation curve at sea level
Curve for blackbody ct 5900
k
0.15
O
3
H
2
O
O
2
H
2
O
Pyranometer sensor
0.10
100
H
2
O
H
2
O
H
2
O
H
2
O
0.05
50
H
2
O, CO
2
H
2
O, CO
2
H
2
O, CO
2
O
3
0
0
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6
1.8 2.0
2.2 2.4
2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2
Wavelength (
μ
)
(b)
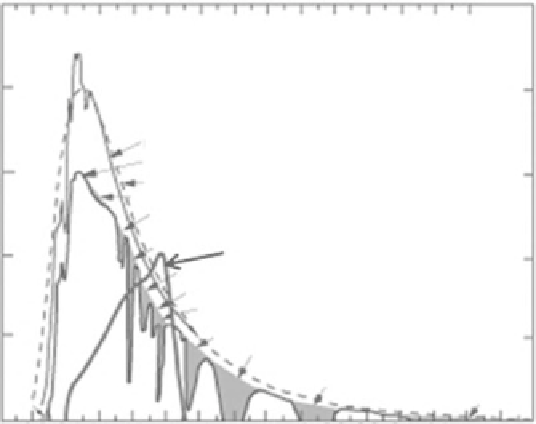
Figure 7.3
(a) Wavelength
dependent response of a
LI-CORR LI-200 photovoltaic
pyranometer compared with
the spectrum of solar
radiation above and below
the atmosphere; (b) LI-COR
pyranometer which uses the
photovoltaic method.
(LI-COR Environmental,
2010; after Federer and
Tanner, 1966.)
Measuring net radiation
Net radiometers differ from pyranometers in that they measure the
difference
between the incoming and outgoing radiant energy in both the solar and the
longwave wavebands. Many net radiometers currently in use measure the net
difference in energy input to two blackened surfaces, one facing up and one down.
Using a thermopile, analogous to the approach used in thermoelectric pyranometers,
the difference in temperature between the two surfaces generates a voltage, see
Fig. 7.4a. The surfaces are commonly protected from the environment (especially
precipitation) by polythene domes which allow radiation of all wavelengths to reach