Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
Altitude
Fundamental to mountain climatology are the changes that occur in the atmosphere
with increasing altitude, especially decreases in temperature, air density, water vapor,
carbon dioxide, and impurities. The sun is the ultimate source of energy, but little heat-
ing of the atmosphere takes place directly. Rather, solar radiation passes through the
atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface. The Earth itself becomes the radi-
ating body, emitting long-wave energy that is readily absorbed by CO
2
, H
2
O, and other
greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Thus, as the atmosphere is heated directly by the
Earth rather than by the sun, temperatures are usually highest near the Earth's surface
and decrease with altitude. Mountains are part of the Earth, too, but present a smaller
land area at higher altitudes within the atmosphere, and so are less able to modify the
temperature of the surrounding air. A mountain peak is analogous to an oceanic island.
The smaller the island and the farther it is from large land masses, the more its climate
will be like that of the surrounding sea. By contrast, the larger the island or mountain
area, the more it modifies its own climate. This
mountain mass effect
is a major factor
in the local climate.
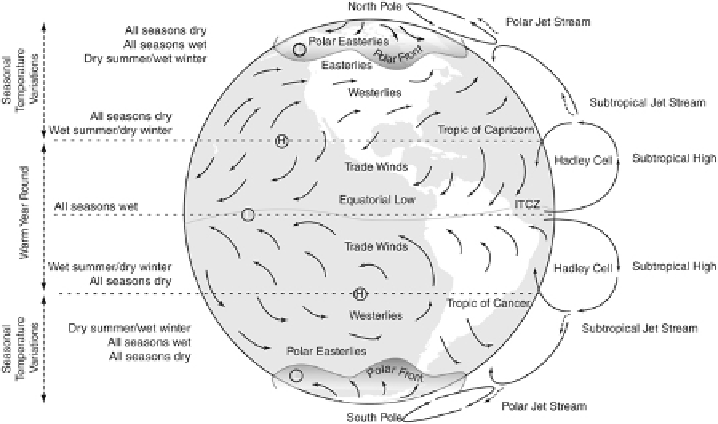
FIGURE 3.2
The general distribution of global atmospheric pressure systems and general circulation
of the atmosphere. These winds dictate global climatic patterns associated with latitude. The gen-
eral latitudinal climatic zones are shown along the right side of the diagram. (Adapted from sev-
eral sources.)
The density and composition of the air control its ability to absorb and hold heat. The
weight or density of the air at sea level (standard atmospheric pressure) is generally
expressed as 1,013 mb (millibars), or 760 mm (29.92 in.) of mercury. Near sea level,
pressure decreases at approximately 1 mb per 10 m (30 mm/300 m or 1 in./l,000 ft) of
increased altitude. Above 5,000 m (20,000 ft) atmospheric pressure begins to fall off ex-
Search WWH ::

Custom Search