Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
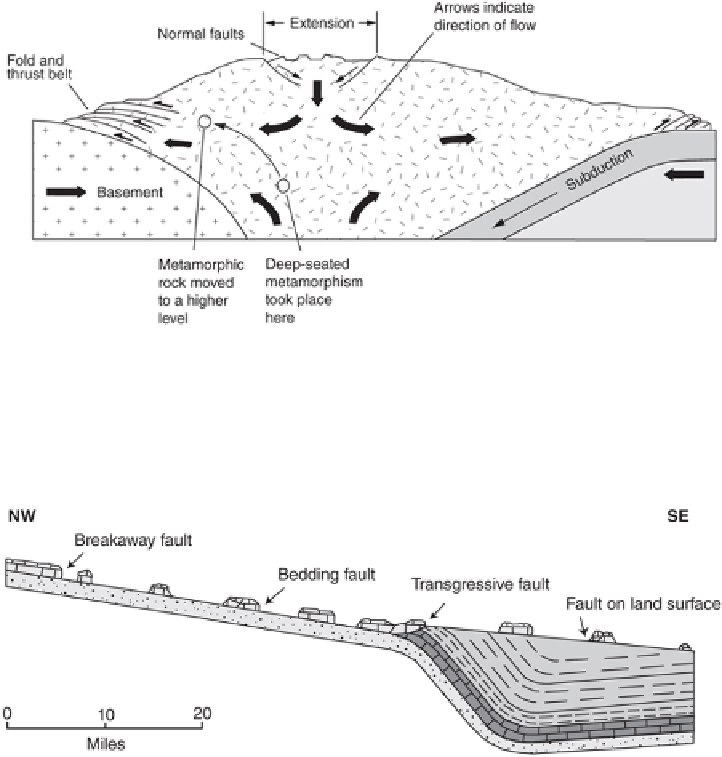
FIGURE 2.28
Cross section of a large collisional mountain range in which gravitational collapse by in-
ternal fracture and flow allow lateral movement of rock outward from the range. Faulting occurs
in surficial brittle rock, whereas rock metamorphosed at depth flows up and out at a higher level
in the mountain belt to replace the mass lost through folding, thrust faulting, and surface erosion.
(After Plummer et al. 2003.)
FIGURE 2.29
Heart Mountain detachment fault, located in northwestern Wyoming near Yellowstone
National Park. Blocks up to 8 km (5 mi) across have broken away from strata at upper left and
slid down the gentle incline so that older strata now rest upon younger rock. The origin of this
structure has been controversial for decades but may have been associated with the massive Ab-
saroka volcanoes and their sector collapses in early Tertiary time. (Adapted from Pierce 1957 and
Garner 1974: 194.)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search