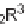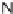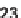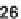Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
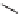
diastereoselectivity; the only exception was the exocyclic diene
14
, presumably due
to the difficulty of achieving the required s-cis conformation. Indeed, in two cases
(
20
and
21
), activation with lithium bis-trifluoromethanesulfonimide in acetone was
required [18]. This activation did not succeed when the azodicarboxylate
16
was used
as a dienophile, and resulted in the formation of the ene-reaction product
22
. The
19 new scaffolds were then used as substrates for subsequent diversity-generating
reactions, such as dihydroxylation and carbamoylation. A small molecule that sup-
presses glycolytic production of ATP and lactate in a CHO-K1 cell line [19] was
discovered.
Recently, Kwon's group reported a branching reaction pathway in which they com-
bined phosphine-catalyzed annulations, Tebbe reactions, and Diels-Alder cycload-
dition reactions to generate skeletal and stereochemical diversity (Scheme 3.7) [20].
Ninety-one heterocyclic compounds, including 16 different scaffolds, were synthe-
sized. Alkoxy dienes
23
and
24
were generated by the Tebbe reaction. They reacted
diastereoselectively with several dienophiles (specifically, benzoquinone, imines,
maleimides, triazolinediones, and tetracyanoethylenes), and produced polycyclic
compounds (e.g.,
25
and
26
) that possessed high chemical diversity in terms of
both scaffold and stereochemical diversity. Several hits targeting breast cancer cells
were found within the library, demonstrating how diversity and complexity might be
more important than library size for success.
In the context of developing new synthetic strategies that may allow for a more
systematic exploration of the chemical space, Nelson's group reported the use of
intra- and intermolecular Diels-Alder cycloaddition reactions in combination with
metathesis cascade chemistry (Scheme 3.8) [21]. The 1,3-dienes (
27
to
29
), gener-
ated through the metathesis cascades, were reacted using three different approaches.
SCHEME 3.7
Branch reaction pathway: combination of Tebbe reaction with Diels-Alder
cycloaddition reaction to generate polycyclic compounds.