Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ultimately regulates cellular proliferation and differentiation [105b]. The noncanon-
ical Wnt pathways regulate downstream gene expression in a
-catenin-independent
manner and are primarily involved in cell migration. These pathways include the
planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway, the Wnt/calcium(Ca
2
+
) pathway, the steroid
receptor binding, and the atypical receptor tyrosine kinase pathway [105a]. Abnor-
mal up-regulation of Wnt pathways has been reported in many types of cancer [106],
and small-molecule inhibitors of the Wnt pathways have been developed as potential
anticancer therapeutics [104a,106b,107]. Meanwhile, diminishedWnt pathway activ-
ity has also been found to be closely associated with diseases such as osteoporosis
and neurodegenerative disorders [108], suggesting that small-molecule activators of
the Wnt pathway would be useful. However, only a few such activators have been
reported [109].
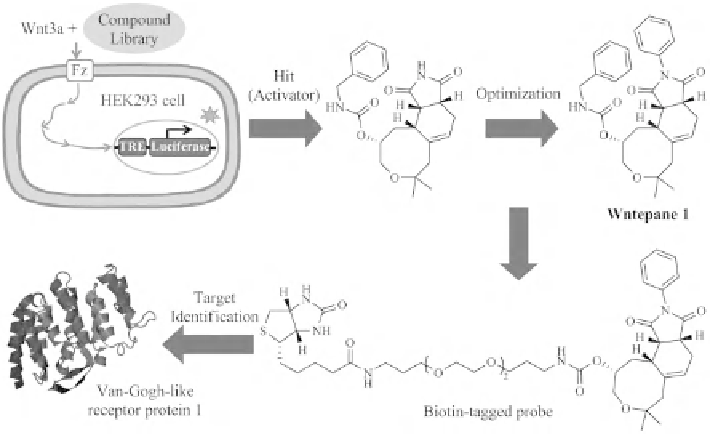
The Waldmann group has identified a new class of Wnt pathway activators, desig-
nated as Wntepanes, using BIOS [96]. To measure the activation of the Wnt pathway,
a stably transfected luciferase reporter cell line derived from HEK293 cell was made
by cotransfection of a plasmid containing Tcf/Lef (Wnt pathway transcription fac-
tors) binding sites followed by the luciferase gene, and a human Frizled-1 (Fz, cell
surface Wnt ligand receptor for enhancing the cells' sensitivity to the Wnt ligand.
The screening of BIOS compounds in this luciferase assay led to the identification
of several hits (the most potent hit is shown in Figure 18.9) that stimulated the
signal synergistically with the canonical Wnt ligand Wnt3a protein. After further
quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) optimization, Wntepane 1 was
found to be the most active Wnt activator, with an ED
50
value of 1.8
±
0.9
M
(Figure 18.9).
FIGURE 18.9
Novel activator of the Wnt pathway developed using BIOS [110].