Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
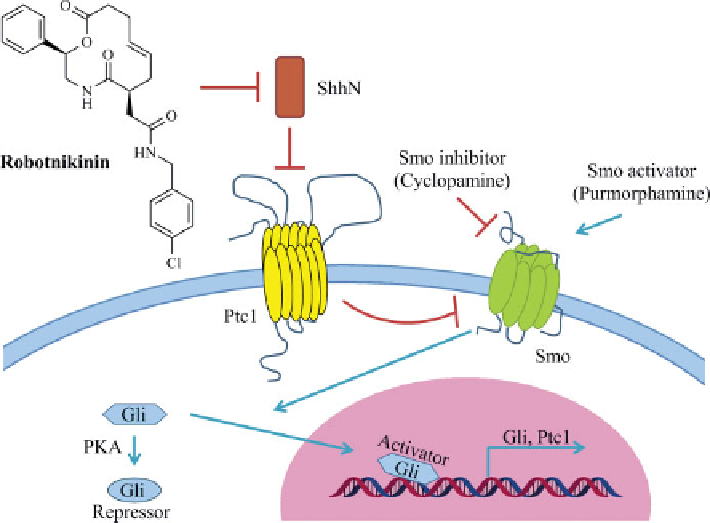
FIGURE 18.1
Robotnikinin inhibits Shh signaling by blocking Shh ligand binding to Ptc1.
(
See insert for color representation of the figure.
)
tumors, such as medulloblastoma in the brain and fibromas in the heart and ovaries
[52,53]. Overactivation of Shh signaling is also reported to play an important role in
the development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) [52].
Schreiber's group screened a DOS library of 2070 compounds arrayed on microar-
rays for binding to bacterially expressed ShhN, leading to the identification of a novel
macrocyclic inhibitor of Shh signaling, robotnikinin [43,55]. An initial hit demon-
strated binding to ShhN in a concentration-dependent fashion by surface plasmon
resonance (SPR) assays and also showed moderate inhibition of the Shh pathway in a
Gli-dependent luciferase assay with Shh-LIGHT2 cells. Optimizations led to the com-
pound robotnikinin, which exhibited low micromolar affinity for ShhN (Figure 18.1).
Robotnikinin's dose-dependent activity in the Shh signaling pathway was confirmed
by its inhibition of ShhN-stimulated alkaline phosphatase induction in C3H10T1/2
cells and its repression of ShhN-stimulated Gli1 and Gli2
m
RNA expression in human
keratinocytes. These results suggested that the inhibitory effect of robotnikinin on
Shh signaling is likely to be a global effect, independent of cell types and reporters.
Coincubation with the Smo agonists (SAG) purmorphamine completely abolished the
inhibitory effect of robotnikinin on Shh signaling, further indicating that the target of
robotnikinin is upstream of Smo [43].
Prior to the discovery of robotnikinin, all of the Shh modulators reported acted on
Smo or targets downstream of Smo. As the first identified inhibitor of the Shh pathway