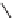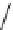Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
NO
2
OH
N
Me
NH
N
O
H
Me
N
Me
Me
9-hydroxyelipticine
OH
90
Selective inhibitor of
HOXA13 DNA interaction
91
Unselective inhibitor of
HOXA13 DNA interaction
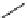
FIGURE 17.16
Selective and nonselective inhibitor of HOXA13 DNA interaction from the
HTS of a pyrrolidinone library and known bioactives.
Screening of this library in a variety of assays revealed that two compounds
inhibit the binding of HOXA13 with DNA. Two pyrollidinones (
90
, Figure 17.16,
and a closely related analog not shown) were identified from the primary screen. The
most potent showed an IC
50
value of 6.5
M while showing no nonspecific binding
to DNA. The lack of nonspecific binding is important, as other compounds (such as
9-hydroxyelipticine,
91
, Figure 17.16) showed activity in the primary screen but are
also known to interact nonselectively with the DNA [71]. Although limited screening
data were available to establish the importance of the library design, the novelty of
finding a micromolar inhibitor of a transcription factor from a primary screen cannot
be ignored.
17.5 CONCLUSIONS
As probe and drug development continue to adapt to new and challenging biologi-
cal targets, diversity-oriented synthesis will serve as an important strategy to access
next-generation small molecules. DOS makes possible systematic access to natural
product-like inspired compounds which incorporate complexity, an important feature
that relates to lower toxicity and a greater chance of success through clinical trials.
DOS-designed libraries incorporate near neighbors and stereoisomers for the gener-
ation of structure-activity relationships and stereostructure-activity relationships in
high-throughput screening campaigns, along with desirable lead-like physicochemi-
cal properties. Modular pathways allow for easy access to all parts of a compound for
medicinal chemistry purposes. Combined, this upfront investment allows access to
novel chemical space, the prioritization of hit compounds, and strategies to develop
lead or probe compounds, and, possibly, novel therapeutics. Although the concept
is still relatively new, progress has shown that DOS will play a valuable role in the
future of drug discovery.