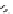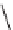Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Bn
(a)
N
N
cyclization
N
OMs
N
O
OMe
66
cytisine
65
(b)
O
O
R
OPg
1
O
R
OPg
1
R
activation
activation
N
O
O
H
at Pg
2
H
at Pg
1
H
Pg
2
O
N
N
Pg
2
O
OMe
O
68
67
69
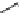
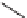
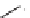
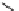
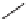
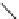
FIGURE 17.14
(a) Key cyclization in the total synthesis of cytisine; (b) key cyclization in a
novel DOS library to access a bridged bicyclic scaffold and a tricyclic scaffold.
of substituted aryl ring systems, still at the meta-position, increasing activity to
nanomolar binding affinity (
63
). Replacing the biaryl motif for a benzyl amine led
to a number of single-digit nanomolar binders, as well as two picomolar binders for
BCL-2 (
64
). Preclinical trials for these lead compounds are still ongoing.
The second such example from Infinity involves a natural product-inspired DOS
library, which also provided novel inhibitors of BCL-2 through an HTS campaign
[64]. Cytisine (
66
), a bridged-bicyclic pyridone natural product, contains a ther-
apeutically relevant motif, as analogs have been used both as antismoking and
antiphospatase therapeutics. A DOS library was designed utilizing a key cycliza-
tion described in the total synthesis of cytosine [65] to form the pyridone motif
(Figure 17.14a). By starting with highly functionalized pyrrolidine (
67
), along with
suitable ester functional groups, access to bridged bicyclic
68
and tricyclic
69
was
achieved (Figure 17.14b).
The synthesis for both scaffolds starts with a [3
+
2] cyclization between com-
mon pyridinium imine
71
and the appropriate
-unsaturated ester using AgOAc
(Scheme 17.8). The resulting pyrrolidine is then subjected to a series of protecting
group manipulations and the key cyclization to afford the scaffolds for library syn-
thesis. Two important aspects should be considered: The chemistry was scalable,
having achieved the synthesis on
,
75 g of material, and the scaffold synthesis was
carried out on both enantiomers of each scaffold, providing valuable SSAR data in
future HTS campaigns. Subsequent capping of the secondary amine with a variety
of different functional groups (R
1
), as well as incorporating different esters, amides,
and carboxylic acids (R
2
) at the carbonyl position, provided closely related analogs
in the library to generate SAR in biological assays. In all, some 15,000 compounds
were prepared with acceptable purities for screening.
>