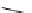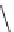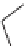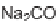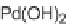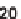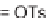Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
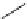
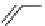
SCHEME 17.4
Preparation of spirotetrahydro
-carboline
25
(spiroindolone
25
).
L/kg), a low total systemic clearance (CL
=
9.75 and 3.48 ml/min/kg) and excellent
bioavailability (
F
100%). Taken together, these properties are compatible with a
once daily oral dosing regimen. In a
P. berghei
malaria mouse model, infection was
cleared completely at a single oral dose of 100 mg/kg. Three daily oral doses of
50 mg/kg also afforded a complete cure. This is significant, as current antimalarial
treatments require drugs to be taken between one and four times a day for up to seven
days; thus the possibility of developing NITD609 into a once-daily oral drug could
make treatment significantly easier in resource-deficient regions.
The goal of this study was to uncover new mechanisms of action in a cell-
based assay. While cell-based screening has many advantages, such as presenting
many targets for the compound to interact with in a biologically relevant setting,
a major hurdle then becomes identification of the target of these small molecules.
An excellent approach to target identification in antimalarials is to apply resistance
selection coupled with next-generation sequencing [47]. In this approach, sublethal
drug pressure is applied to a parasite strain until resistance to the drug is developed.
Analysis of the genome of the drug-resistant strain can reveal the basis for resistance
and the target of the compound. When a similar strategy was applied by Novartis
researchers using NITD609 and the Dd2 parasite strain, it was discovered that three
to four months of constant drug pressure was required to observe a 7- to 24-fold
decrease in IC
50
values. This high number of passages to achieve modest resistance
could be interpreted as a positive attribute of the drug and suggests that the parasites
have difficulty developing resistance. Importantly, none of the resistant parasites
showed cross-resistance to a panel of known antimalarial agents, further suggesting
=