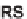Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
as chemical tools to further explicate the complex biology of
-cells and can also
lead to novel medicines against diabetes. Chou et al. developed a phenotypic assay
to identify small molecules that can prevent cytokine-induced
-cell apoptosis [20].
They also developed a number of secondary assays to further characterize the small
molecules identified through the phenotypic screen.
When the primary assay was conducted in the HTS mode, two different types
of small-molecule collections were screened: (1) the Molecular Libraries Small
Molecule Repository (MLSMR) collection and (2) a DOS-derived library at the
Broad Institute. The MLSMR collection consists of over 300,000 small molecules
derived primarily from commercially available small molecules. This collection was
rich in heterocycles, had lower Fsp
3
content, and in general had scaffolds that are
less complex in terms of both chemical architecture and stereochemical elements
[11]. In contrast, the DOS collection screened in this assay was rich in medium-sized
rings, had higher Fsp
3
content, and in general had more complex scaffolds, each with
several stereocenters.
The synthesis of a representative DOS library included in this assay is described in
Scheme 17.1 and was carried out in the Chemical Biology Platform at the Broad Insti-
tute using a build/couple/pair strategy [16c]. The synthesis began with the build phase
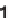
and utilized the anti-selective Abiko asymmetric aldol reaction [21] between
1
and
the protected amino acetaldehyde. After hydrolysis and protection of the secondary
alcohol, the anti
-amino acid derivative
RS-3
was obtained. The corresponding syn
SO
2
Mes
SCHEME 17.1
Build and couple to a linear template
6
.