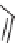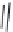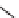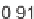Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
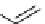
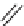
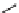
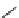
FIGURE 16.2
Exemplary activity cliffs involving structural relationships of different nature.
The activity cliff at the top is formed by two vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2
antagonists that are only distinguished by a single nitrogen substituent (yielding a MACCS
Tanimoto similarity of 1.0). The cliff at the bottom is formed by two cyclooxygenase-1
inhibitors. Here, a central ring system is replaced. These two inhibitors also yield a high
MACCS Tanimoto similarity value of 0.91, but the structural similarity of the cliff-forming
compounds is much more remote than in the other case.
throughout. In addition, it is also important to avoid the use of inappropriate molecular
descriptors. For example, multiproperty molecular representations that increasingly
abstract frommolecular structure are not suitable for the analysis of activity cliffs. As
a general guideline, any calculated similarity that cannot be immediately appreciated
on the basis of two-dimensional molecular graphs should be avoided to characterize
activity cliffs (and activity landscapes). The use of such descriptors tends to “flatten”
activity landscape and separate partners of chemically reasonable cliffs.
As an alternative to Tanimoto similarity, hierarchical structural relationships
between active compounds, Bemis and Murcko scaffolds [37], and cyclic skele-
tons [38] might be utilized as similarity criteria for cliff formation. Starting from
complete molecules, Bemis and Murcko scaffolds abstract from R-groups but retain
linker fragments between rings. Cyclic skeletons further abstract from Bemis and
Murcko scaffolds by converting all heteroatoms to carbon and setting all bond orders