Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
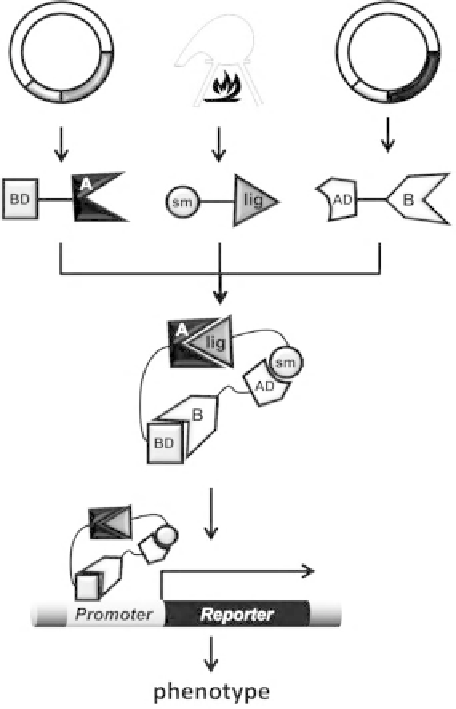
FIGURE 14.7
Y3H assay. Three chimeric entities are needed. The chemical chimera consists
of the compound investigated covalently bound to a known ligand of protein B. The second
chimera consists of protein B and one part of the transcription factor. The third chimera
consists of the second part of the transcription factor and protein A, whose targeting by the
chemical compound under investigation is assayed. If the entire complex gets assembled, the
transcription factor is functional, thus expressing the measurable reporter gene.
binding proteins was demonstrated in a study by Becker et al. [59] designed to
explore the targets of small-molecule-inhibiting kinases. In this study they showed
that the Y3H assay gave useful insights into the characterization of the interaction of
ATP-competitive active-site kinase inhibitors with both serine/threonine and tyrosine
kinases. The findings that interactions with affinities in a range of pharmacological
interest as kinases can be detected with Y3H suggest that this assay can be used in the
context of a broader range of synthetic small molecules. Since the chemical chimera
can be substituted for by a bifunctional small molecule, this approach is useful to
assess the biological activity of such compounds [60].