Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
MDL Drug Data Repostory (below MW 600)
Cyclooxygenase-1 Inhibitors
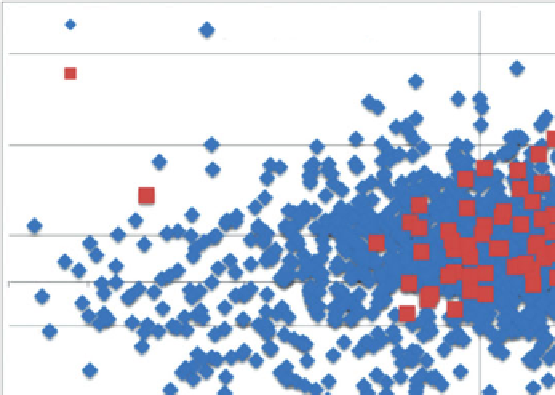
FIGURE 1.3
Chemical space analysis plot of cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) inhibitors (red
squares) and MDDR compounds (blue diamonds), created using chemical descriptors and
principal components analysis. The plot shows that COX-1 inhibitors occupy a wide range of
chemical space. (
See insert for color representation of the figure
.)
strategies are not orthogonal to each other, and many DOS campaigns will contain
aspects of both. Reagent-based diversification (also known as a
branching reaction
pathway
) can be used at any stage of a DOS; it can be used in the early stages to create
diverse functionality or in later stages to transform prefunctionalized molecules into
distinct molecular scaffolds. Generally, there are considered to be two approaches to
reagent-based diversification: the use of “pluripotent” functionality, where a single
functional group can be transformed under a range of reaction conditions to give
distinct functionality or molecular scaffolds; and the use of densely functionalized
molecules, where different functional groups can be transformed orthogonally. The
latter approach is generally used to pair functional groups and so create diverse
molecular skeletons [19,30]. Substrate-based diversification is generally used in the
later stages of a DOS to react strategically placed functional groups intramolecularly
and so
fold
compounds into distinct molecular structures. For this reason, it is often
referred to as a
folding reaction pathway
.
Some of these ideas were further refined by Schreiber when he identified the
use of a
build/couple/pair strategy
as a common feature in the production of small-
molecule collections for biological screening [42]. In the
build
stage, the required,
ideally chiral starting materials are synthesized or obtained from the chiral pool.
These starting materials are then
coupled
together to produce densely functional-
ized molecules; multicomponent reactions are often used at this stage to couple
three or more building blocks together. The
pair
stage then involves intramolec-
ular reactions of the attached functional groups to generate distinct molecular