Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
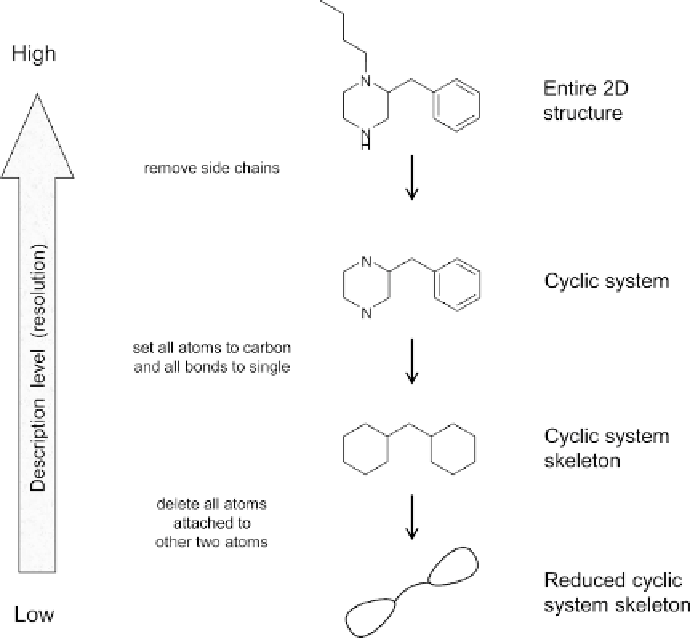
FIGURE 10.6
Example of scaffold definition (cyclic system) usingMEQI. The cyclic system
skeleton and reduced cyclic system skeleton of one chemical structure exemplifies different
levels of structural resolution. The highest level corresponds to the entire two-dimensional
structure. Removal of all side chains leads to the cyclic system level. Setting all nonhydrogen
atoms to carbon and all bonds to single generates cyclic system skeletons. Finally, deleting
all nonhydrogen atoms attached to two nonhydrogen atoms yields reduced the cyclic sys-
tem skeletons, which is the lowest level of structural resolution. The curved lines designate
multibond links connecting the ellipsoidal objects, which represent general ring structures,
while the corresponding straight lines represent single bonds.
resolution and consists of entire molecules, including side chains. From this simple
example it can be seen that as the level of structural resolution increases, moving
down the tree, the number of chemotypes increases, and correspondingly, the number
of structures belonging to each chemotype class decreases. Of note, each chemotype
at a given level of the hierarchy represents an equivalence class. Equivalence classes
partition the set of molecules so that molecules of a given chemotype do not lie in
any other chemotype class at the same level of structural resolution [111].
Measuring and comparing the scaffold diversity of compound collections is not a
trivial task. First, it depends on the specific approach to generating the scaffolds,