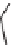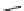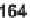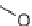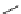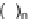Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
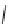
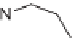
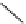
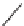
SCHEME 9.19
Application of an oligomer-based approach in the synthesis of skeletally
diverse macrocycles: (a) PyBOP, DIPEA, CH
2
Cl
2
, 71 to 96%; b) BH
3
-DMS, THF, 65
◦
C;
10% Na/K tartrate, MeOH, 88 to 98%; (c)
166
,Et
3
N, CH
2
Cl
2
, 88 to 99%; (d) CsF, DMF,
85
◦
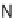
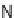
C; or TBAF, NH
4
F; NaH, THF, 62 to 99%; (e) 3-azidobutanoic acid, PyBOP, DIPEA,
CH
2
Cl
2
; TBAF, THF, 72 to 93%; propargyl bromide, NaHMDS, THF, DMF,
−
78
◦
C, 91 to
96%; (f) [Cp
∗
RuCl]
4
, toluene, 70
◦
C (1,5-triazole) or PS-CuPF
6
, toluene, 55
◦
C (1,4-triazole),
56 to 78%; (g)
167
, DIPEA, CH
2
Cl
2
; TBAF, THF; NaH, allyl bromide, DMF, 50 to 77%; (h)
Hoveyda-Grubbs's second-generation catalyst (10 mol%), 5 mol% benzoquinone, toluene, 40
to 60
◦
C, 45 to 93%.
160
and the aldol products
161
by amide formation and subsequent reduction
(Scheme 9.19) [42a]. The amines
162
were then combined with additional building
blocks that were suitably armed to allow subsequent macrocyclization. Macrocyliza-
tion was then effected by nucleophilic aromatic substitution (e.g.,
→
163
), Huisgen [3
+
2] cycloaddition (e.g.,
→
164
), or ring-closing metathesis (
→
165)
. The modular