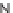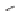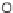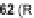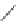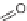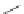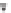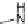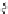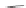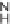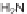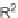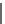Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
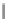
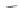
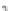
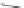
SCHEME 8.11
Rapamycin analogs combining a simplified FKBP binding domain and a
variable peptidic region.
8.5.1 Diversification of Rapamycin
Rapamycin (
61
, Scheme 8.11) and FK506 are bifunctional molecules that pre-
associate to their target FKBP12, then bind to calcineurin and mTOR, respectively.
Part of the bifunctional molecule binds to FKBP12 while the other part serves as
an effector on the third partner. Pei and co-workers generated rapamycin analogs
that combine a simplified FKBP binding domain and a variable peptidic region, as
exemplified by scaffolds
62
and
63
, in order to identify new partners of these com-
plexes via the creation of composite binding surfaces on FKBP12 [81]. Building
on the dimethyl-2-ketobutytyl-L-pipecolate fragment as a minimal FKBP12-binding
fragment, the authors incorporated this fragment into a 200-membered library based
on scaffolds
62
and
63
synthesized on solid phase. Compounds were subsequently
tested for binding to FKBP12. Of 200 compounds tested, 163 bound to FKBP12 with
IC
50
=
M. This library of rapamycin analogs, in complex with FKBP12, has
the potential to serve as an enabling tool to design composite surfaces able to probe
shallow protein-protein interactions or to explore binding sites for kinases outside
the highly conserved ATP-binding site and open new avenues to fine-tune specific
kinase pathways.
2to93