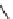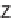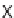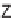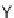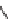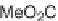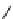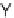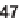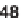Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
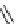
SCHEME 8.8
Diversity-oriented synthesis of macrocyclic peptidomimetics using “click
chemistry.”
compounds. Interestingly, the approach provides two synthetically related classes of
macrocycles that differ by their degree of rigidity and topology. Thus,
46
can be
obtained from
45
by diketopiperazine formation. Diversity stems from the choice
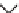
of building blocks
47
and
48
, which governs the orientation and chemical nature of
appendages as well as ring size. Building block assembly used standard peptide cou-
pling, whereas macrocyclization was performed by “click” chemistry following the
build/couple/pair (B/C/P) scheme developed by Nielsen and Schreiber [66]. Using
principal components analysis (PCA), the authors demonstrated that this collection
of 12 analogs covered a distinct and broad chemical space compared to a set of 657
approved drugs.
8.4.3 Macrocyclic Peptoid Libraries
Peptoids (N-alkylated glycine oligomers) are known to be proteolytically stable
and can be accessed easily with broad diversity. They have been associated with
increased cell permeability compared to native peptides [67]. Grubbs and co-workers
recently reported the optimization of a synthetic method for solid-phase synthe-
sis of cyclic peptoids (Scheme 8.9). The authors reported high RCM yields of
precursor
49
to yield resin-supported macrocycle
50
using the Hoveyda-Grubbs