Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
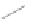
SCHEME 8.6
Complementary approach based on an
m
RNA display to achieve the synthesis
of a library of 10
13
macrocycles consisting of the general structure
31
.
A complementary approach based on
m
RNA display (Scheme 8.6) [50] involved
anchoring of the peptide to puromycin and subsequent elongation using ribosomal
translation. Subsequently, the side chain of lysine was linked to the N-terminal amine
of the peptide using bis-succinimidyl glutarate, followed by RNA cleavage to com-
plete the synthesis of macrocycles
31
. The authors reported the synthesis of a massive
library of more than 10
13
members using this approach. Recently, Yamagishi et al.
reported the synthesis of a ribosome-expressed library of N-methylated macrocyclic
peptides, which delivered an inhibitor of ubiquitin ligase [51].
Phage display has also been used to provide massive libraries of cyclic peptides
closed via a disulfide linkage. Recently, Heinis et al. reported the synthesis of a library
of more stable bicyclic macrocycles by phage display [52]. Compared to the chem-
ically labile disulfide-linked macrocycles, these bicyclic macrocycles incorporate a
stable 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene bridge (Figure 8.3) that simultaneously links three Cys
residues. This library led to the isolation of a new class of inhibitors of kallikrein
(
32
), with an IC
50
value of 20 nM.
In summary, several methods are available for the generation of diversity in macro-
cyclic peptides, ranging from small to very large rings. Macrocyclic peptides are
generally associated with higher chemical and biological stability than that of their
linear analogs. The accessible diversity is limited only by the availability of natu-
ral and unnatural amino acids. The technologies discussed above are amenable to
the production of massive libraries, such as those performed on phage or oligonu-
cleotides, provided that both synthetic schemes and biological testing are compatible
with the presence of such entities. Similarly, robust encoding methods have signif-
icantly simplified the deconvolution required compared with early diversity-based
methodologies (see also Chapter 11). Nevertheless, the peptidic character of these
types of macrocycles will probably remain a limiting factor for their direct use as