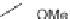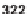Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
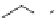
SCHEME 7.44
Synthesis of trisubstituted piperazinones, piperazines, and their unsaturated
analogs. Reagents and conditions: (i) 50% TFA/DCM, rt, 30 min; (ii) TFA/TES/DCM (5 : 1 : 4),
rt, 30 min.
unrelated carbocycles. While treatment of the precursor
319
with TBAF-cleavage
cocktail resulted in ene product
320
, cleavage in TFA led to rearrangement and for-
mation of tricycle
321
, which was also obtained using Wang resin and TFA-mediated
cleavage. Both isolated compounds were screened for antibacterial activity assay.
An analogous strategy of scaffold hopping portrays the conversion of resin-bound
precursors
322
or
323
into nitrogenous heterocycles, depending on cleavage condi-
tions. TFA solution in DCM and solution of TFA with addition of a reducing agent
(TES) afforded different heterocycles (Scheme 7.44) [81]. Iminium ions were trans-
formed to 3,4-dihydropyrazin-2(1
H
)-ones
324
and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrazines
325
(in the case of TFA-mediated cleavage) or by formation of piperazin-2-ones
326
or piperazines
327
(in the case of TFA/TES-mediated cleavage). Piperazinones and
piperazines are known to be important pharmacophores [82].
7.7 CONCLUSIONS
In this chapter we have described numerous approaches to arriving at diverse com-
pounds using polymer-supported synthesis, including skeletal-, stereochemical-, and
appendage diversity-generating processes. We focused mainly on skeletal diversity,
due to its great potential to create diverse heterocyclic compounds, although a com-
bination of strategies such as those described in the B/C/P method provides the most
promising potential for diversity creation. In our opinion the critical advantage of the
use of solid-phase chemistry for DOS resides in a potential to build (and synthesize) a
large number of very diverse compounds in a relatively short period of time together
with the operational simplicity of the process (remember, isolation of intermediates
after each reaction step takes about 5 minutes!). Obviously, the chemistry needs to
be optimized and robust enough to afford reasonable purity of target compounds.
Because solid-phase chemistry does not allow the purification of intermediates, the
purity of crude products depends on the entire sequence of individual reaction steps.
However, one should not be discouraged if one reaction in the entire sequence does