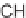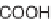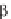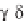Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
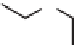
FIGURE 6.2
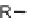
Skeletal and stereochemical diversity to bicyclic compounds by tuning the
starting compounds from the chiral pool and the cyclization process.
A collection of such constrained dipeptide isosteres were used as probes to dissect
their effects on a panel of
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
strains as a model to screen
the activity of these compounds toward cell growth [33]. Specifically, we conceived
the screening of wild-type strains and selected deletants involved in multidrug resis-
tance using cell growth as the phenotype of study. This selection process through
phenotypic screening on yeast strains enabled the selection of library member
089
,
which was identified as the molecule inducing the most intense cell growth decrease.
6.4.4.2 DOS of Morpholine-Containing Scaffolds
In a second application of a
library of peptidomimetics in chemical genetics studies, we generated a new set
of morpholine-based compounds to be screened toward yeast strains. Following
the diversity-oriented synthesis of morpholine scaffolds, and taking advantage of a
two-step process involving the combination of amino acid derivatives as building
blocks, a high degree of chemical diversity was achieved around such heterocycles.
Specifically, the reactivity of the acetal moiety and the amino and carboxylic groups
of the parent amino acid component was exploited with a series of acid-mediated
reactions (Scheme 6.14) [34]. Specifically, constrained mono-, bi-, and tricyclic
scaffolds were obtained from a linear densely functionalized intermediate taking
advantage of lactone or lactam formation, and of trans-acetalization reactions.