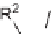Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
SCHEME 6.13
Diversity pathways to morpholine scaffolds through the application of
-
amino acid derivatives to a couple/pair approach. (From [34], with permission of John Wiley
& Sons; copyright
C
2009 John Wiley & Sons.)
several bioactive molecules, such as MMP and TNF inhibitors [29], and is found in the
structure of tricyclic benzodiazepines [30] and of 8,6-fused bicyclic peptidomimetic
compounds such as interleukin-1
-converting enzyme inhibitors [31]. The strategic
approach to the generation of morpholine scaffolds encompassed the application of
-amino acid derivatives such as amino carbonyls (path i) and amino acetals (path
ii), or using
-amino alcohols (path iii) to be coupled with suitable building blocks
possessing complementary functionalities to achieve structurally diverse heterocycles
after the cyclization step (Scheme 6.13).
6.4.4.1 Bicyclic Peptidomimetics
During the last decade we reported several
papers on the generation of bicyclic compounds from a combination of sugar or
tartaric acid and amino acid derivatives. The synthetic process consisted of two key
couple/pair steps: the coupling of two components from the chiral pool, followed by
an intramolecular cyclization to achieve the bicyclic structure [32].
This class of bicyclic compounds showed structural similarity to dipeptides, allow-
ing for their application as suitable molecular platforms for peptidomimetic chemistry.
Morever, a wide array of molecules bearing such a bicyclic moiety was achieved with
skeletal and stereochemical diversity by tuning the starting compounds from the chi-
ral pool and the cyclization process, and was obtained as readily available constrained
amino acids for insertion in peptide structures (Figure 6.2).