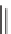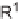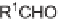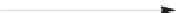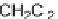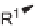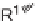Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Now more than ever, there is a need for the development of structurally novel
chemical entities to keep pace with the ever-evolving field of biomedical sciences
[4]. Over the past several decades, many technological advances in synthetic organic
chemistry have contributed to a more ambitious design as well as the practical
generation of diverse chemical libraries [5]. For example, single-mode microwave
heating has moved into the mainstream synthetic laboratory, and flow chemistry is
rapidly following suit. This chapter is not intended to be either a comprehensive
review of domino reactions or a chemical library synthesis but, rather, a compilation
of some recent applications of domino reaction sequences in the design of unique
chemical libraries.
5.2 PERICYCLIC DOMINO REACTIONS
Based on a previously reported resin-linked two-component-domino-Knoevenagel-
ene reaction [6], Tietze et al. reported the solid-phase synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrans
3
and
4
via a domino-Knoevenagel-hetero-Diels-Alder sequence (Scheme 5.1) [7].
This intermolecular three-component reaction was performed similar to a one-pot
reaction without the requirement of workup and purification of intermediates. The
utilization of solid-supported chemistry allowed for the use of reagent excesses that
were required for driving the equilibrium to reaction completion. Knoevenagel con-
densation of the polymer-bound acetoacetate
1
with aliphatic aldehydes (5 equiv)
in the presence of catalytic piperidinium acetate provided polymer-bound oxabu-
tadienes
2
. Treatment with enol ethers (10 equiv) and heating in pressure flasks
for three days was required to achieve the inverse electron-demand hetero-Diels-
Alder cycloaddition. Cleavage from the resin utilized a basic trans esterification with
sodium methoxide to afford methyl-3,4-dihydro-2
H
-pyran-5-carboxylates
3
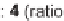
and
4
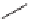
SCHEME 5.1
Synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrans
3
and
4
via a domino-Knoevenagel-hetero-
Diels-Alder sequence.