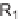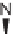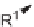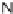Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
the phosphine-mediated [3
2] annulations, suggested a new reaction mechanism.
In addition, the loss of SO
2
was observed with the
p
-nitrobenzene attached to the
γ
+
-carbon. Aryl-substituted aziridines worked very well with good-to-excellent yield
and good 1,2-trans-diastereoselectivity. Electron-withdrawing or electron-donating
groups in the ortho, meta, and para positions were all well tolerated. Loss of diastere-
oselectivity occurred when an alkyl-substituted aziridine was used, whereas the
unsubstituted aziridine gave poor yield. It is noteworthy that these tetrahydropy-
ridines can be functionalized further through the NH and both ester groups.
Bauer et al. developed a unique approach to yield 10 different classes of polycyclic
scaffolds using transition metal-mediated cycloaddition and cyclization reactions of
enynes and diynes (Scheme 3.35) [61]. A
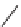
t
-butylsulfinamide [62] group (
100
,
101
)
was used as a unique lynchpin, due to the fact that it gives asymmetric induction
during substrate synthesis, can be deprotonated and
N
-alkylated, and can readily be
deprotected or oxidized. The authors performed a reactivity study in several transition
metal-mediated reactions of the enynes and diynes and found that these substrates
were suitable for Ru-, Co-, Rh-, and Ni-catalyzed reactions. Among over 25 reac-
tions investigated, eight appeared to be selective and efficient for library production.
All enynes readily underwent Pauson-Khand reaction, yielding [5,5]-bicyclic
SCHEME 3.35
Transitionmetal-mediated cycloaddition and cyclization reactions of enynes
and diynes.