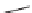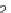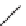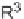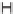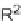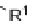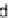Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
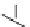
FIGURE 3.4
Suggested mechanism for intramolecular nitrone cycloaddition reaction.
(Adapted from [46], with permission; copyright
C
2010 American Chemical Society.)
trans orientation at positions 2 and 3 were assigned for
84
from coupling constants
and NOE measurements. Additional evidence of this conformation is the fact that
the substituent at positions 2 and 8 are both quasi-equatorial, whereas in the
si
side
attack they are quasi-axial.
Several recent studies have focused on synthesizing collections of small molecules
containing privileged scaffolds [47]. Privileged scaffolds are particular frameworks
with drug-like and versatile binding properties, which lead to high hit rates and more
drug-like libraries. In these efforts, Martin et al. recently reported the design and
synthesis of a DOS pathway that combines a Mannich-type multicomponent assem-
bly process (MCAP) [48] with several pairing cyclization reactions to afford highly
functionalized heterocyclic ring systems. Benzodiazepine-, tetrahydropyridine-, aryl
piperidine-, and tetrahydroisoquinoline-based scaffolds were synthesized. A ther-
mally induced intramolecular Huisgen [3
2] cycloaddition reaction generated the
1,2,3-triazole-1,4-benzodiazepine scaffold
85
, which was further functionalized
through
N
-diversification [49]. Using silyl-protected enols in MCAP, a free alde-
hyde was generated that, upon heating with
N
-methylhydroxylamine, underwent an
intramolecular dipolar cycloaddition reaction, which generated the isoxazolidine
86
as a single diastereomer. Condensation of the aldehyde with sarcosine, followed by
thermolysis of the oxazolidinone intermediate, afforded the pyrrolidine-fused scaf-
fold
87
(Scheme 3.27) [50].
When a tetrahydroisoquinoline core was introduced in a MCAP, a series of com-
plex heterocyclic scaffolds were synthesized in which tetrahydroisoquinolines are
fused to quinazolone, dihydropyrimidine-2,4-dione, 1,4-diazepine-2,5-dione, and
1,5-benzodiazepin-2,5-dione rings (Scheme 3.28) [51]. 7-Bromodihydroisoquinoline
88
was used for these MCAPs, because it allowed for further functionaliza-
tion via cross-coupling reactions. The three-component reaction of
88
,
trans
-
crotonyl chloride, and silyl enol ether catalyzed by TMSOTf provided the aldehyde
89
. Then the aldehyde underwent intramolecular nitrone cycloaddition when
N
-
methylhydroxylamine was added, affording isoxazolidine
90
. Compounds with this
tricylic ring system are potent
+
α
2
-adrenoceptor antagonists [52]. Moreover, when
88
reacted with either zinc phenylacetylide or ethynylmagnesium bromide, the inter-
mediate generated was trapped with
o
-azidobenzylchloride to yield an amide. Upon
warming to room temperature, the amide easily underwent a [3
+
2] cycloaddition