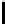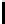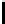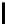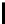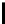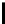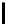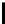Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 10.7
The Function
PC
1 of the DES
57 49 41 33 25 17 9
1 8 0 2 4 6 8
0 2 9 1 3 5 7
9 1 3 0 2 4 6
63 55 47 39 31 23 15
7 2 4 6 8 0 2
4 6 1 3 5 7 9
21
13
5
28
20
12
4
Table 10.8
The Function
PC
2 of the DES
14 17 11 24 1 5
3 28 15 6 21 10
23 19 12 4 26 8
6 7 7 0 3 2
41
52
31
37
47
55
30
40
51
45
33
48
44
49
39
56
34
53
46
42
50
36
29
32
be reversed, meaning that the DES round keys must be used in reverse order (i.e.,
k
16
,...,k
1
) to decrypt a given ciphertext.
12
10.2.1.4
Security Considerations
Since its standardization in the 1970s, the DES has been subject to a lot of public
scrutiny. For example, people found that there are 4 weak keys and 12 semiweak
keys.
•
ADESkey
k
is
weak
if
DES
k
(
DES
k
(
m
)) =
m
for all
m
64
,
meaning that the DES encryption with
k
is inverse to itself (i.e., if
m
is
encrypted twice with a weak key, then the result is again
m
).
∈M
=
{
0
,
1
}
•
The DES keys
K
1
and
K
2
are
semiweak
if
DES
k
1
(
DES
k
2
(
m
)) =
m
for all
m
64
, meaning that the DES encryptions with
k
1
∈M
=
{
0
,
1
}
and
k
2
are
inverse to each other.
12
Test vectors for DES encryption and decryption can be found, for example, in a NIST document
available at http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/nistpubs/800-17/800-17.pdf.