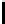Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
Ta b l e 8 . 2
Truth Table of the Logical Functions Employed by MD4
XYZf gh
000000
001101
010001
011110
100001
101010
110110
111111
a second time and the resulting FIPS PUB 180-2
13
superseded FIPS PUB 180-1
beginning February 1, 2003. In addition to superseding FIPS 180-1, FIPS 180-2
also added three new algorithms that produce and output larger hash values (see
Table 8.1). The SHA-1 algorithm specified in FIPS 180-2 is the same algorithm
as specified in FIPS 180-1, although some of the notation has been modified to
be consistent with the notation used in SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512. As
summarized in Table 8.1, SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512 produce and
output hash values of different sizes (160, 256, 384, and 512 bits), and their maximal
message sizes, block sizes, and word sizes also vary considerably. In February 2004,
the NIST published a change notice for FIPS 180-2 to include SHA-224.
14
SHA-224
is identical to SHA-256, but uses different initial hash values and truncates the final
hash value to its leftmost 224 bits. It is also included in Table 8.1.
In addition to the cryptographic hash functions proposed by RSA Security,
Inc., and the NIST, there are at least two competing proposals developed entirely in
Europe (i.e., RIPEMD-128 and RIPEMD-160 [15, 16]). These cryptographic hash
functions are not further addressed in this topic.
MD4, MD5, and RIPEMD-128 produce hash values of 128 bits, whereas
RIPEMD-160 and SHA-1 produce hash values of 160 bits. The newer versions of
SHA produce hash values that are even longer. From a security viewpoint, long hash
values are preferred (because they reduce the likelihood of collisions in the first
place). Consequently, it is recommended to replace MD5 with SHA-1 (or any other
hash function from the SHA family) where possible and appropriate. MD4, MD5,
and SHA-1 are overviewed and discussed next.
13
http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/fips/fips180-2/fips180-2.pdf
14
SHA-224 is also specified in informational RFC 3874 [14].