Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
IPH
E
RTEXT )
( C
Stream cipher
key
A
N
EJ
W
I
L
Q
. . .
generator
PLAI
NTEXT
RD
A
Y
C
O
W
T
L
. . .
block cipher
key
. . .
Algorithm
Algorithm
Algorithm
R
. . .
KLA
T
E
X
T
X
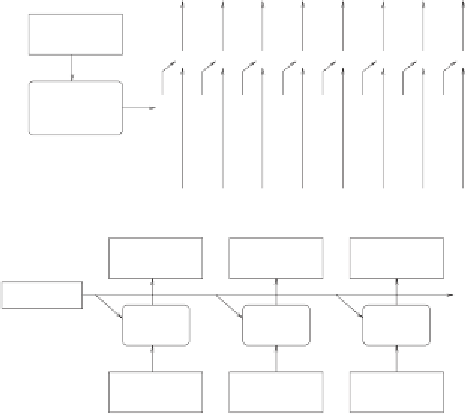
Figure 4.2:
Block ciphers and stream ciphers.
Stream ciphers and block ciphers are also told apart by their purposes of use,
which are not strictly defined. You can actually use a block cipher similarly to
a stream cipher (e.g., in OFB mode; see Section 5.1.1).
We will look only at block algorithms in the following discussion.
4.1.4 Product Algorithms
Most modern block ciphers are
product algorithms
: simple, cryptologically
relatively insecure steps are made one after the other. Such a step is called a
round
. You've already come across a seven-round product method. To really
confuse you I'll describe it like this:
•
The first round is a polyalphabetic substitution with period 26. A fixed
substitution scheme is rotated cyclically by 1 in each position of the
period, which results in 26 substitutions.
•
The second round is similar, except 26 substitutions follow one another
(and are rotated only then), which results in a period length of 26
2
=
676.